The changing climate, on the one hand, is bringing many ancient microbes to life. However, on the other hand, a constant rise in the rates of infection occurrences is being observed. Among these, bacterial infections occupy a prominent place. Among many types of skin infections, those causing pain, scarring, and needing treatment are of greater concern. In this article, 9 commonly occurring bacterial infections on the skin have been enlisted.
Following are the 9 commonly occurring bacterial infections on the skin
1. Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a pain-causing bacterial skin infection that affects the dermis along with subcutaneous tissues. It affects the skin at a deeper level and causes redness and thus is erythematous.
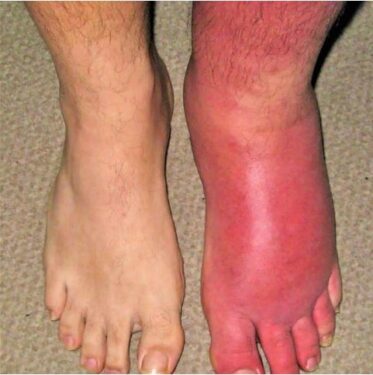
Cellulitis affected the foot in comparison to the normal one
Causative agents
The most common causative agents of cellulitis are Staphylococcus and Streptococcus bacteria.
Site of occurrence
Cellulitis most commonly affects the following areas:
- The area surrounding the surgical wounds
- Injured sites with open wounds
- Location of an existing tinea infection
Apart from these, cellulitis can occur on the skin of:
- Face
- Neck
- Hands
- Buttock
- Feet
- Legs
- Torso
Symptoms
Its common symptoms are:
- High fever
- Mounting white blood cell count
- Edema
- The feeling of warmth at the infection site
- Constantly advancing borders
- Ulceration
Treatment
After diagnosing the cellulitis, your physician will prescribe the most suitable antibiotics for you. However, the therapy is different for diabetic and non-diabetic patients. If the patient does not have diabetes, the first-line therapy must include:
- Penicillinase-resistant penicillin
- First-generation cephalosporins
- Augmentin (Amoxicillin-Clavulanate)
- Macrolide antibiotics
- Fluoroquinolones
In case of diabetes or any other inflammatory and immunocompromising disorder, aspiration of the affected area is preferred. Along with this, second or third-generation cephalosporins can be prescribed.
2. Erysipelas
Erysipelas, also known as St. Anthony’s fire, is a bacterial skin rash of intense nature. The margins of the infected site are well-defined and raised. Young kids, the elderly population, alcoholics, diabetics, as well as immunocompromised individuals are at a higher risk of contracting erysipelas.
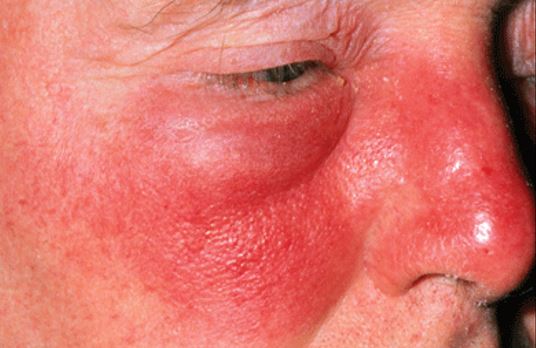
Erysipelas-affected facial skin
Causative agents
The causative agent of erysipelas is Beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
Site of occurrence
Erysipelas mostly affects:
- Face
- Legs
Symptoms
The symptoms leading to the diagnosis of erysipelas include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Painful, warm, swollen, raised sores on the skin with defined boundaries
- Influenza-like symptoms
Treatment
Apart from the administration of intravenous penicillin, the rest of the treatment options for erysipelas are similar to those used for cellulitis.
3. Impetigo
Impetigo is a bacterial infection that causes a rash on the skin. It can be characterized by the presence or absence of bulla i.e. bullous or non-bullous. Bullae are yellowish serous-fluid filled which, upon rupture, leave behind a reddish ring on the affected area. The high-risk group includes children between the ages of 2 to 5 years old.
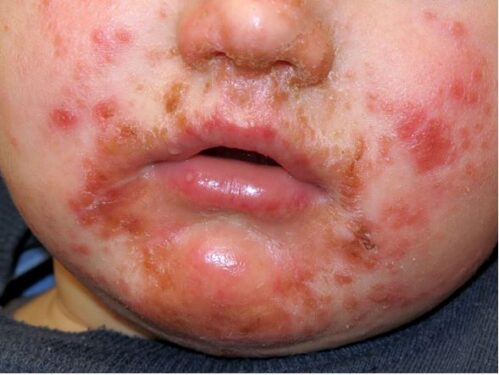
Impetigo
Causative agents
Staphylococcus aureus is the culprit behind this bacterial rash.
Site of occurrence
Impetigo can occur in any part of the skin.
Symptoms
The symptoms of non-bullous impetigo include:
- Erosive skin texture
- Honey-yellow ooze-filled sores
- Edema
- Hypertension
- Glomerulonephritis
- Smoky or tea-colored urine
However, in the case of bullous impetigo, fluid-filled thin-walled bulla are visible and have a diameter of 2 to 5 cm.
Treatment
Treatment options for impetigo include:
- Application of topical mupirocin (Bactroban) ointment (twice a day for 5 days)
- Azithromycin for 5 days
- Cephalexin for 10 days
- Dicloxacillin
- Oxacillin
- Amoxicillin-Clavulanate
- Fluoroquinolones
- Erythromycin
4. Folliculitis
Folliculitis can occur as a result of a physical injury, damage to the hair follicles, chemical irritation, or an infection. People who have experienced acne problems in the past are more prone to folliculitis.
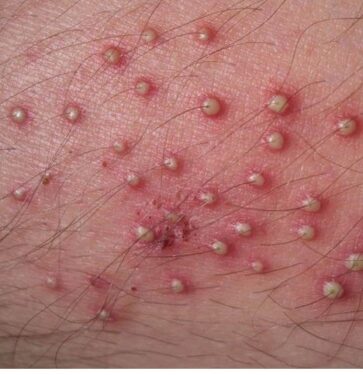
Folliculitis
Causative agents
The following can be the causative agents of folliculitis:
- Streptococcus aureus
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Klebsiella
- Enterobacter
- Proteus
- Yeast
- Fungi
Site of occurrence
Folliculitis can occur at the following parts:
- Head
- Face
- Neck region
- Truck
- Buttocks
- Extremities
Symptoms
Patients with folliculitis exhibit the following symptoms:
- Fever (although rare)
- Itching on the affected area
- Blisters filled with pus
Treatment
Superficial folliculitis is painless and does not leave a mark after healing. If folliculitis is deep in the skin, the following antibiotics can be given:
- Clindamycin
- Mupirocin
- Macrolides
- Fluoroquinolones
Benzoyl peroxide can also be administered to aid the healing process.
5. Furuncles
A furuncle is a bacterial infection rash characterized by the development of pus-filled boils on the skin. It affects the hair follicles, hair shaft, as well as sebaceous glands. Its size keeps on changing with time as more and more pus accumulates in it and gives rise to an ‘abscess’.
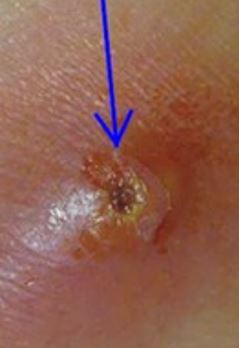
Furuncles
Causative agents
Its causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus.
Site of occurrence
Furuncles occur at the following points:
- Face
- Neck
- Armpits
- Buttock
- Thighs
Symptoms
The symptoms of furuncles are:
- Fever
- Malaise
- Painful lesions on the skin
Treatment
In order to extract the fluid out of the boil, the application of a warm compress, along with iodoform gauze, can be helpful. If the condition is more severe, surgical removal of the pus might be needed. Moreover, the following antibiotics can also be administered via the parenteral route:
- Cloxacillin
- Cefazolin
6. Carbuncles
A carbuncle is a contagious bacterial rash on the skin. These are formed when multiple furuncles appear at an area like a cluster covering an area as large as 4 inches.
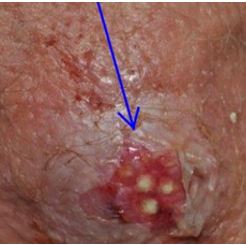
Carbuncles
Causative agents
Its causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus.
Site of occurrence
Carbuncles occur at the following points:
- Back of the neck
- Back
- Thighs
Symptoms
The symptoms of carbuncles are:
- Fever
- Malaise
- Painful lesions on the skin
Treatment
Like in the case of furuncles, the application of a warm compress along with iodoform gauze is the first-line treatment for carbuncles. However, in the case of carbuncles, the treatment is difficult and takes a longer time. Furthermore, the physician may also recommend surgical removal of the pus. Moreover, the first-generation cephalosporins can also be administered via the parenteral route.
7. MRSA infections
An MRSA bacterial infection is characterized by the appearance of pus-filled bumps on the skin which are painful and warm to the touch. It is contagious in nature.
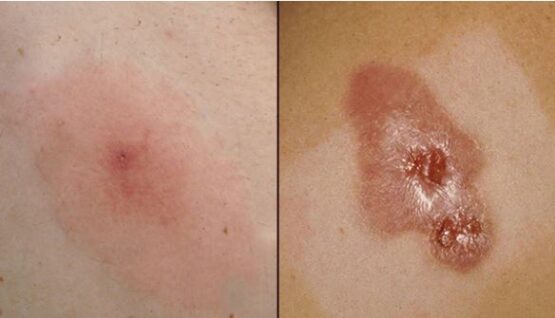
MRSA infection
Causative agents
The causative agent of this bacterial rash is Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Site of occurrence
The common sites of occurrence for an MRSA infection are:
- Nose
- Back of the throat
- Armpits
- Groin
- Existing wounds
Symptoms
The symptoms of MRSA are:
- Redness
- Inflammation
- Pain
- Pus
- Fever
Treatment
As MRSA is resistant to most of the antibiotics, it is hard to treat its infection. However, the following drugs may help in the treatment:
- Neomycin
- Linezolid
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
8. Erythrasma
Erythrasma is an itchy bacterial skin rash. It persists for a longer time and particularly affects hair, nails, sweat, and sebaceous glands.
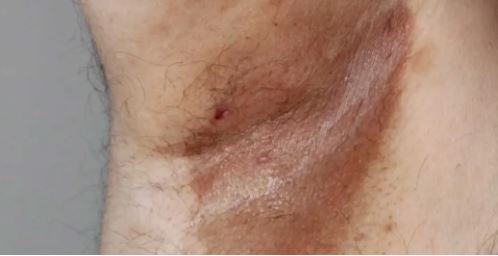
Erythrasma
Causative agents
The causative agent of erythrasma is Corynebacterium minutissimum.
Site of occurrence
The common sites of occurrence for an erythrasma infection are the skin folds in the inguinal as well as axillary regions.
Symptoms
The symptoms of erythrasma are:
- Red, pinkish, or brown patches
- Scaly skin texture
- Cracked skin
Treatment
The following are the best treatment options for erythrasma:
- Fusidic acid topical cream
- Miconazole cream
- Erythromycin for 4 days
- Clindamycin
9. Leprosy
Leprosy or Hansen’s disease is one of the oldest bacterial diseases. It progresses over time and becomes hard to treat if worsened.
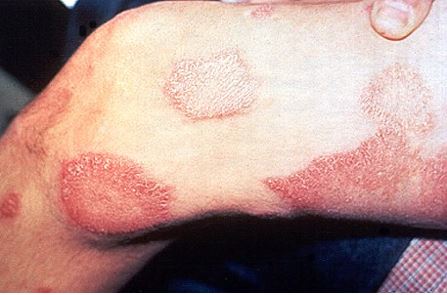
Leprosy
Causative agents
Its causative agent is Mycobacterium leprae.
Site of occurrence
Leprosy occurs at:
- Nerves of extremities of the skin
- The lining of the nasal cavity
It can also progress to the upper respiratory tract.
Symptoms
The symptoms of leprosy are:
- Muscular weakness
- Skin lesions
- Numbness of hands, feet, legs, and arms
Treatment
To treat leprosy, multidrug therapy is used which includes:
- Dapsone
- Rifampin
- Clofazimine
- Minocycline
- Ofloxacin
Conclusion
Bacterial infections are a common occurrence in these days and age as the world has still not been able to completely eliminate microbial contamination. These bad bacteria, when enter the body, causes several infections including those affecting the skin. In this article, a compilation has been given of 9 such bacterial infections which are being caused by different bacteria and are spreading in various countries in 2023. It is good to know their symptoms, self-diagnose in case of a skin rash, and decide if you need to visit your physician.

PhD Scholar (Pharmaceutics), MPhil (Pharmaceutics), Pharm D, B. Sc.
Uzma Zafar is a dedicated and highly motivated pharmaceutical professional currently pursuing her PhD in Pharmaceutics at the Punjab University College of Pharmacy, University of the Punjab. With a comprehensive academic and research background, Uzma has consistently excelled in her studies, securing first division throughout her educational journey.
Uzma’s passion for the pharmaceutical field is evident from her active engagement during her Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) program, where she not only mastered industrial techniques and clinical case studies but also delved into marketing strategies and management skills.
Throughout her career, Uzma has actively contributed to the pharmaceutical sciences, with specific research on suspension formulation and Hepatitis C risk factors and side effects. Additionally, Uzma has lent her expertise to review and fact-check articles for the Health Supply 770 blog, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information presented.
As she continues her PhD, expected to complete in 2025, Uzma is eager to contribute further to the field by combining her deep knowledge of pharmaceutics with real-world applications to meet global professional standards and challenges.








