As soon as the COVID cases start to rise every time, a need to take the COVID test for flu-like symptoms is generated. The physicians recommend these tests based on the patient’s condition after making a preliminary checkup.
However, a patient can also take a test if she or he feels the need. There are several COVID-19 tests with varying degrees of reliability that can be taken to confirm or rule out the possibility of the disease.
A reliable test is one which has been approved by the WHO and is being conducted according to the guidelines issued by the FDA. Let us take a look at which COVID tests are currently available, how are they performed, and why are they important.
A technician holding a sample for the COVID test
Types of COVID-19 tests
Tests that can be conducted for the COVID-19 virus can be classified into two categories:
1. Polymerase chain reaction
Polymerase chain reaction, commonly known as PCR or RT-PCR test, is considered the most reliable test which can be done for the SARS-CoV virus. The working principle of a PCR test is NAAT i.e. the nucleic acid amplification test. Due to its high accuracy and superiority over antigen tests, it is often termed a ‘gold standard’ for all other COVID tests.
How is it performed?
The PCR test is designed to detect the presence of viral genetic material in a person’s fluid sample. For this purpose, reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction is used. The test is conducted in the following steps:
- A sample is collected from a person using a nasopharyngeal swab. With the help of this swab, the nasal fluid from the back of the nasal cavity is obtained. Sample can also be taken from the oral cavity with the help of an oropharyngeal swab or, in some cases, a person might be asked to give a saliva sample by spitting into a tube.
- The collected sample is then run through the PCR machine which separates and amplifies the viral DNA or RNA if detected.
- Results are obtained within 3 days.
Significance
A PCR test provides the following advantages:
- A PCR test is accurate enough to detect the coronavirus in asymptomatic patients as well apart from the reliable results provided for the symptomatic ones.
- A single PCR test is enough to confirm or rule out the possibility of a COVID infection.
Limitations
Despite many advantages, a PCR test also has the following limitations:
- A PCR test is, overall, a time-consuming process as it takes usually 3 days to get the results after the test has been taken.
- PCR test usually costs much higher than rapid antigen tests thus making them inaccessible for a lot of patients.
- A PCR test can only be taken at a lab or a testing site. Only well-trained personnel can run the test after taking a sample.
2. Antigen tests
Antigen tests are rapid tests that are known for giving results within 15 to 30 minutes. The results, although accurate, do not dominate PCR tests in terms of reliability.
How is it performed?
The rapid antigen tests are performed based on the following guidelines:
- For a rapid antigen test, like PCR, the nasal fluid sample is needed which is collected using a nasal swab. It should be made sure that the swab stays in the nasal cavity for at least 15 seconds. For some tests, a blood sample might also be required.
- The sample is then transferred to the sample port and 2 to 3 drops of buffer solution are added.
- Wait for 15 minutes until the test strip indicates a positive or a negative result.
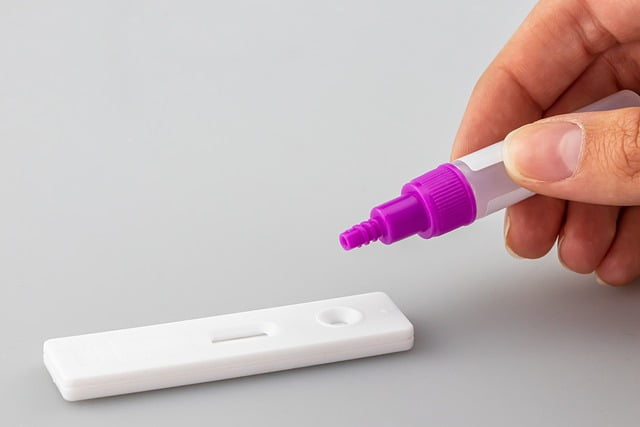
The buffer being added on the rapid antigen test strip
Rapid test kits for COVID-19 are available at Health Supply 770 at the most affordable prices. Make sure to place an order to get the best deals on every medical item.
Significance
When compared to PCR tests, the rapid antigen tests provide the following advantages:
- The results of an antigen test are usually more accurate for a positive result. However, in case of a negative result, the possibility of an infection cannot be ruled out easily. The FDA recommends taking 2 rapid antigen tests with a gap of 48 hours for individuals with symptoms. For those who are asymptomatic, the test should be done thrice over a period of 2 days.
- A rapid antigen test does not need the services of trained personnel to be conducted. Rather, it can be performed as a self-test at home by the patient or by the patient’s family member.
- A rapid antigen test gives the results within 30 minutes thus it is time-saving and quick.
- The cost of a rapid antigen test is much lesser than that of a PCR test.
Limitations
A rapid antigen test cannot reliably detect the COVID virus in an asymptomatic patient i.e. the chances of a false-negative result are higher. In such cases, the test has to be performed again and again based on the testing guidelines issued by the FDA.
Comparison of PCR and rapid antigen test
The following table provides a comparative analysis of the PCR and rapid antigen test:
| Parameters | Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) | Rapid antigen test |
| Principle | NAAT | Detection of viral proteins |
| Place of conduction | Testing lab | Home-based |
| Services of trained personnel | Required | Not required |
| Reliability | Higher than antigen tests | Less than the PCR test |
| Sensitivity | Highly sensitive | Less sensitive |
| Repetition | Not required | Required based on the FDA guidelines |
| Time required to get the results | 3 days | 15 to 30 minutes |
| Cost | Higher | Affordable |
Conclusion
Many types of COVID-19 tests are available in the market these days. Two of these include PCR tests and rapid antigen tests. PCR is the most reliable between both the testing options but requires more time to give the results.
On the other hand, antigen test gives results quickly but there is a higher chance of a false-negative result. Although both tests vary based on their reliability, sensitivity, and cost, both are extensively used to confirm or rule out the possibility of a COVID infection.

PhD Scholar (Pharmaceutics), MPhil (Pharmaceutics), Pharm D, B. Sc.
Uzma Zafar is a dedicated and highly motivated pharmaceutical professional currently pursuing her PhD in Pharmaceutics at the Punjab University College of Pharmacy, University of the Punjab. With a comprehensive academic and research background, Uzma has consistently excelled in her studies, securing first division throughout her educational journey.
Uzma’s passion for the pharmaceutical field is evident from her active engagement during her Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) program, where she not only mastered industrial techniques and clinical case studies but also delved into marketing strategies and management skills.
Throughout her career, Uzma has actively contributed to the pharmaceutical sciences, with specific research on suspension formulation and Hepatitis C risk factors and side effects. Additionally, Uzma has lent her expertise to review and fact-check articles for the Health Supply 770 blog, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information presented.
As she continues her PhD, expected to complete in 2025, Uzma is eager to contribute further to the field by combining her deep knowledge of pharmaceutics with real-world applications to meet global professional standards and challenges.