In healthcare setups, the most critical job is to provide care to a patient admitted in the emergency which is correctly referred to as a race against time. The first and foremost task is to save the life of the patient followed by a huge challenge aimed at minimizing the aftereffects of the injury or trauma. Patients may become paralyzed, lose their ability to hear or get trapped in a life-long struggle with their wounds. Thus, to prevent or at least reduce the chances of such incidents, it is important to treat the patient effectively with the best interventions at hand. One such intervention is bundled care therapy which is employed in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Let us briefly look into what acute intracerebral hemorrhage is and what kind of handling is best suited for it.
What is an intracerebral hemorrhage?
Intracerebral hemorrhage or ICH, commonly known as a brain bleed, is a condition in which bleeding occurs within the brain. This can be due to the rupturing of blood vessels surrounding the cranium thus resulting in the leaching of the blood directly into the brain. This pool of blood can further become a cause of stroke or can even be fatal.
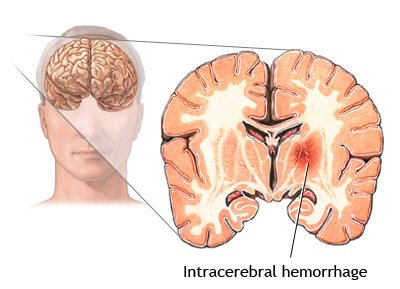
Intracerebral hemorrhage
Causes of intracerebral hemorrhage
The most common causes of intracerebral hemorrhage are:
- Constant hypertension
- Infections within the brain
- Tumors within the brain
- Atherosclerosis i.e. hardening of the blood vessels due to fat buildup
- Coagulopathy i.e. a condition in which the blood clotting process is impaired
- Head injury or trauma e.g. tripping, falling, being hit by a solid object, etc.
- Cerebral arteriovenous malformation
- Brain aneurysm i.e. a bulging inflammatory tissue of the arteries surrounding the brain
- Cerebral amyloid angiopathy i.e. a fatal condition in which amyloid-beta is accumulated within the brain
- Eclampsia
- Seizures
- Abnormal collagen formation
Brain scans showing the hemorrhagic area
Symptoms of intracerebral hemorrhage
The common symptoms of intracerebral hemorrhage are as follows:
- Severe headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Loss of vision
- Seizures
- Dysphagia
- Neck stiffness
- Loss of balance
- Tingling or numbness of the face, arms, and legs
- Unexplained weakness
- Difficulty in speech and perception i.e. aphasia
- Confusion
- Loss of alertness
- Drowsiness
- Abnormal heart rate
Bundled care therapy for ICH
The bundled care therapy provided in case of acute intracerebral hemorrhage includes the following interventions:
- Control of blood pressure: Lowering systolic blood pressure and its maintenance at 140 mm Hg or less is the first and foremost concern in the healthcare setups. It has been found that although the lowering of blood pressure is a significant intervention, it alone cannot reduce the mortality rate or improve quality of life unless paired with other interventions.
- Maintenance of body temperature: Maintenance of body temperature at 37°C (99.5°F) is of critical importance. For this purpose, anti-fever medications are administered with the aim of treating any fever or hyperthermia.
- Treatment of hyperglycemia: Hyperglycemia or increased blood glucose level must be treated and reduced to a level of 110 to 140 mg/dL or 6.1 to 7.8 mmol/L for patients with no history of diabetes. However, for diabetics, a value between 140 to 180 mg/dL or 7.8 to 10.0 mmol/L is acceptable.
- Reversal of abnormal anticoagulation: Lastly, a rapid reversal of warfarin-related abnormal anticoagulation is needed. Its normal ratio must not exceed 1.5.
Bundled care therapy vs the usual care
In comparison to the usual care provided to ICH patients, the protocols related to bundled care therapy have been found to be far more efficient:
- Bundled care therapy lowers the risk of worse functional outcomes in patients with acute ICH by 14%.
- A significant reduction has been observed in the mortality rate within the first 6 months of the trauma.
- Adverse effects experienced by the patients treated with bundled care therapy comprise 16.0% as compared to those experienced by the patients treated with usual care therapy for ICH i.e. 20.1%.
Prevention of intracerebral hemorrhage
Although it is not impossible to treat ICH, it is easier to prevent it. By a simple modification of one’s lifestyle habits, the goal of preventing a hemorrhage is not a further one. These modifications include:
- Maintain normal blood pressure. In case of abnormalities, keep monitoring your B.P. If it is constantly high, consult your physician.
- Keep monitoring your blood sugar level. If you are diabetic, maintaining a normal BGL value leads to a significantly reduced chance of getting affected by intracerebral hemorrhage.

Lifestyle habits to minimize the risk of ICH
- Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight. Lower your cholesterol levels by doing work out.
- If you are on anticoagulants, frequently take the test to measure clotting time. Keep in touch with your doctor to talk about your medications and their possible side effects.
- Eat healthy and nutritious food. Avoid fatty and junk food.
- Quit smoking and alcohol.
- Wear a helmet to prevent a head injury in case of an accident.
Conclusion
Intracerebral hemorrhage, although a rare condition, is hard to manage and treat. The unavailability of top-notch treatments and healthcare facilities especially in the smaller setups has rendered the provision of primary ICH care even tougher. However, with bundled care therapy, the day-to-day treatment interventions can be used in a collective way to maximize the efficiency of therapy. This way, not only the side effects as well as the mortality rate associated with ICH have been reduced, but also the quality of life of the patients has significantly improved with the use of a minimum healthcare budget.

PhD Scholar (Pharmaceutics), MPhil (Pharmaceutics), Pharm D, B. Sc.
Uzma Zafar is a dedicated and highly motivated pharmaceutical professional currently pursuing her PhD in Pharmaceutics at the Punjab University College of Pharmacy, University of the Punjab. With a comprehensive academic and research background, Uzma has consistently excelled in her studies, securing first division throughout her educational journey.
Uzma’s passion for the pharmaceutical field is evident from her active engagement during her Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) program, where she not only mastered industrial techniques and clinical case studies but also delved into marketing strategies and management skills.
Throughout her career, Uzma has actively contributed to the pharmaceutical sciences, with specific research on suspension formulation and Hepatitis C risk factors and side effects. Additionally, Uzma has lent her expertise to review and fact-check articles for the Health Supply 770 blog, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information presented.
As she continues her PhD, expected to complete in 2025, Uzma is eager to contribute further to the field by combining her deep knowledge of pharmaceutics with real-world applications to meet global professional standards and challenges.