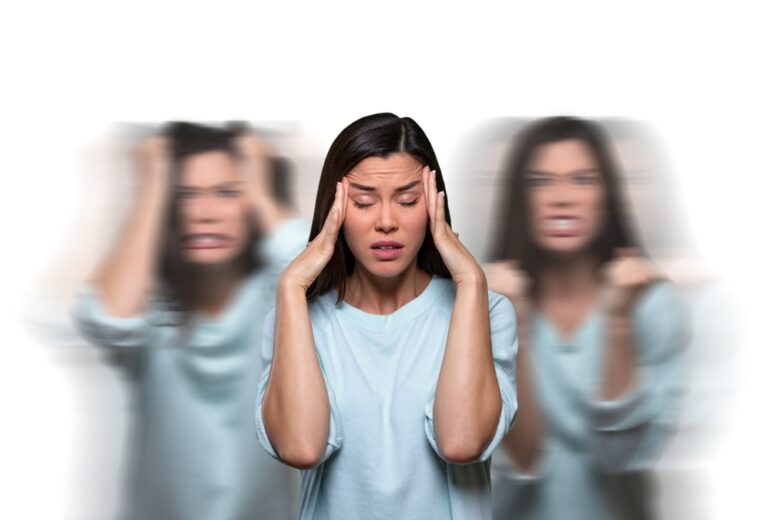
Among the gravest disorders affecting the human species in this day and age, mental health disorders occupy a bigger chunk. There is an exponential increase in cases when it comes to mental health problems which, however hard to diagnose, massively risk the person’s well-being. One such disorder is borderline personality disorder. Let us take a look at what it is and what are its types.
What is borderline personality disorder?
Borderline personality disorder, abbreviated as BPD, is a mental health issue affecting a person’s ability to perceive emotions about one’s own self resulting in an altered sense of functionality in daily life. The domains highly impacted by borderline personality disorder include:
- Perception of one’s self-image
- Management of emotions
- Expression of behaviors
- Stability in relationships

Borderline personality disorder
A person, affected by BPD, has a strong fear of abandonment and rejection by other people. Most of the time, these individuals, knowingly or unknowingly, start to self-isolate or their impulsive behavior restricts people from coming close to them. As a result, no friendship or any sort of relationship lasts more than a few months.
Signs and symptoms of BPD
The signs and symptoms of BDP include:
- The presence of a strong fear of abandonment at all times is one of the signs of BPD which results in a behavior where the person maximizes her or his efforts to avoid rejection.
- An important factor among the other BPD signs is the distortion of self-image. A person’s goals and values constantly keep on shifting. Moreover, the person feels about one’s own self as a bad and unnecessary presence.
- Among the other borderline personality disorder symptoms, a rapid shift occurs in a person’s idea about other people i.e. at one moment, if a person is being considered ideal and perfect, the very next moment, that same person is perceived as cruel.
- It is common to experience moments of paranoia during which the relationship with reality is totally cut off for a limited period of time.
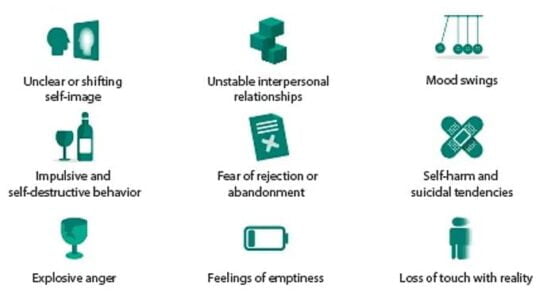
Symptoms of BPD
- The patterns of self-harm leading to suicidal thoughts are also associated with borderline personality disorder.
- The signs of borderline personality disorder also include mood swings where a period of extreme happiness is followed by feelings of anxiety, shame, or irritability.
- Other BPD symptoms include a constant feeling of emptiness, unexplained anger, and sarcastic behavior leading to bitterness, as well as indulging in fights.
- People with BPD are often found involved in binge eating, gambling, alcoholism, over-speeding, drug abuse, and taking instant decisions about important aspects of life.
Causes of BPD
The main causes of BPD include:
- Genetic factors: A person may be more prone to borderline personality disorder if her or his genes suggest so. People who have mental health disorders present in close family members such as parents or siblings become at high risk of BPD as well as other mental health conditions.
- Abnormalities within the brain: Research has suggested that physical changes within the brain, such as variations in the levels of neurotransmitters e.g. serotonin, can be a prominent cause of BPD.
- Stressful childhood: People who have gone through traumatic experiences as children are at higher risk of developing BPD.
Types of BPD
According to classification, there are four different types of BPD which include:
- Discouraged borderline personality disorder: The discouraged BPD or quiet BPD is marked by the existence of feelings of guilt and shame. The individual expresses serious issues of emotional attachment. Social anxiety is prominent. The person gets obsessed with certain actions, ideas, or people and a feeling of inadequacy always remains.
- Impulsive borderline personality disorder: Individuals with impulsive BPD are prone to the feeling of immediate gratification followed by a period of anger and dissatisfaction afterward. It is common for such people to feel rejected by the society.
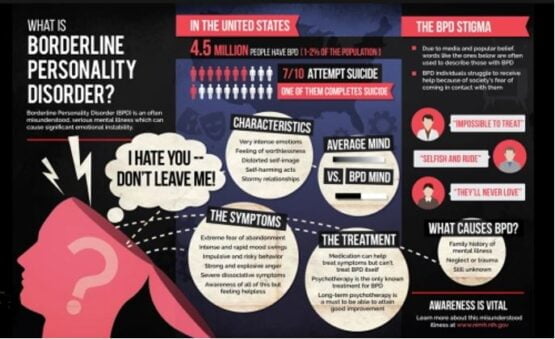
Overview of BPD
- Petulant borderline personality disorder: Petulant BPD gives rise to individuals who possess shaky emotions. They lack stability in their mood and can become aggressive very easily. Their self-image is considered by them as full of faults. They also express a controlling behavior over others.
- Self-destructive borderline personality disorder: The self-destructive BPD pushes the affected individual towards self-hatred, self-harm, substance abuse, and ultimately suicidal thoughts start developing. Such people are hard to talk to as they express bitter behaviors towards others and thus are bad at making new friends or relationships apart from sabotaging the existing ones.
How to identify BPD?
These borderline personality disorder types can be diagnosed by a physiotherapist and treated accordingly. Although a self-diagnosis can be done even successfully in some cases, it is advised to seek the help of a healthcare professional. There are certain tests that are conducted to further differentiate the BPD types and subtypes. These include:
- Personality assessment inventory (PAI)
- APA’s diagnostic manual of mental disorders (DSM-5)
How to treat BPD?
The therapy for BPD is dependent on a person’s age and the extent and severity of the issue. The therapeutic options include:
- Dialectical behavior therapy: Dialectical therapy helps the person to be present in the moment instead of drifting away in her or his thoughts. This helps in the management of extreme emotions.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy: Cognitive behavioral therapy focuses on the modification of the thoughts and actions of the person impacted by BPD.
- Schema-focus therapy: The schema-focus therapy helps the person to envision her or his self positively and helps to eliminate negativity about one’s own self.
- STEPPS: STEPPS or the ‘Systems Training for Emotional Predictability and Problem Solving’ makes the person aware of the tools she or he can use for the management of reactions to day-to-day afflictions. The success of STEPPS also requires the training of family members and close friends.
Conclusion
The borderline personality disorder, or as it is also called, the emotionally unstable personality disorder is one of the leading mental health problems today. Once rightly diagnosed, BPD requires proper therapy to improve the patient’s situation. Moreover, it is of great importance to keep track of your thoughts and actions if you fall into the high-risk group. Remember, a mental health disorder, although fully treatable, can be avoided.

PhD Scholar (Pharmaceutics), MPhil (Pharmaceutics), Pharm D, B. Sc.
Uzma Zafar is a dedicated and highly motivated pharmaceutical professional currently pursuing her PhD in Pharmaceutics at the Punjab University College of Pharmacy, University of the Punjab. With a comprehensive academic and research background, Uzma has consistently excelled in her studies, securing first division throughout her educational journey.
Uzma’s passion for the pharmaceutical field is evident from her active engagement during her Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) program, where she not only mastered industrial techniques and clinical case studies but also delved into marketing strategies and management skills.
Throughout her career, Uzma has actively contributed to the pharmaceutical sciences, with specific research on suspension formulation and Hepatitis C risk factors and side effects. Additionally, Uzma has lent her expertise to review and fact-check articles for the Health Supply 770 blog, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information presented.
As she continues her PhD, expected to complete in 2025, Uzma is eager to contribute further to the field by combining her deep knowledge of pharmaceutics with real-world applications to meet global professional standards and challenges.








