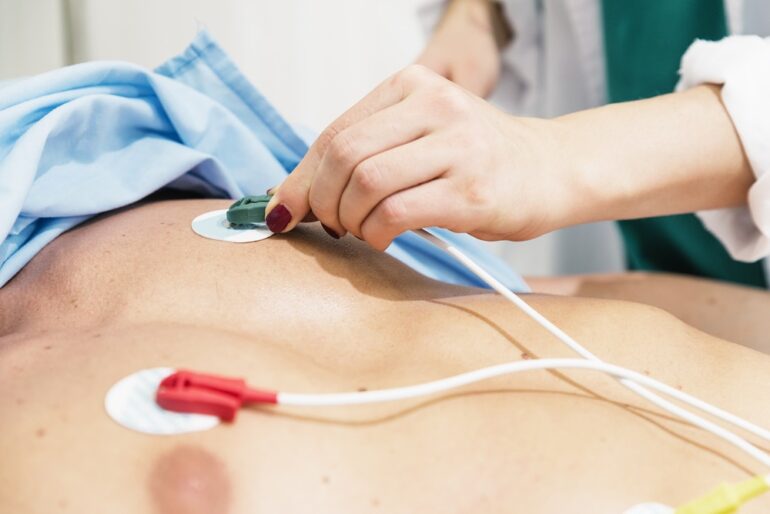
Every day, several patients contact their physicians to report minor or major ailments to which the physicians respond by running certain tests before prescribing medications. One of these frequently recommended tests is electrocardiography. An electrocardiography is a process employed for electrocardiographic measurement which is accurate in indicating the current state of the heart in terms of its physiology as well as anatomy. Let us take a look at what exactly an ECG is and what is the role of the electrodes used in it.
What is ECG?
ECG is an abbreviation for ‘Electrocardiography’, a technique used to quantify the electrical conduction of the heart. It is a quick, reliable, economical, as well as relatively simple test that gives an accurate account of the state of a person’s heart i.e. whether it is healthy or diseased.
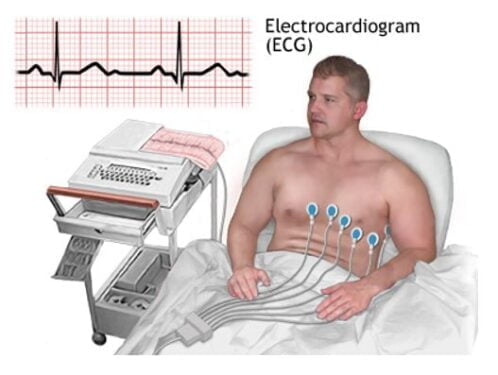
An ECG test being run on a patient
How to conduct an ECG?
To conduct an ECG, electrodes are placed over the chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes are further connected to the ECG machine via a lead wire which transmits the signals detected by the electrodes to the machine where they are recorded and interpreted. Furthermore, a graph is generated by the ECG machine which is referred to as an electrocardiogram.
ECG electrodes
The use of electrodes in the process of ECG is of prime importance as they are the receivers of the electrical signals of the heart. Their number as well as material vary over a wide range which affects the efficiency of the test.
Materials used in making the ECG electrodes
The commercially available electrodes used in ECG are made up of stainless steel filled with silver chloride solution with a soft plastic pad to stick the electrode with the skin.
Types of ECGs based on the number of electrodes used
ECG can be conducted in three ways using different numbers of electrodes. Therefore, an ECG classification can be made based on the quantity and positioning of the electrodes which is given below:
- 12-Lead ECG: 12-Lead ECG is conducted using 10 electrodes among which 6 are placed onto the chest and the other 4 are placed onto the soft tissue of the limbs. This is the most accurate method.
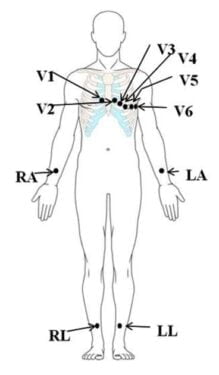
(Where Vs=Points on the chest region, RA=Right arm, LA=Left arm, RL=Right leg, and LL=Left leg)
- 5-Lead ECG: It uses one precordial electrode which is to be placed onto the chest in addition to four electrodes for placement onto the limbs (i.e. RA, RL, LA, LL, Chest).
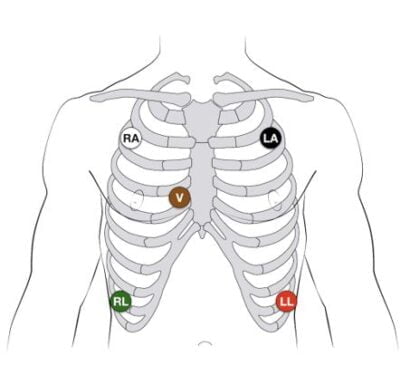
(Where V=Point on the chest region, RA=Right arm, LA=Left arm, RL=Right leg, and LL=Left leg)
- 3-Lead ECG: It uses three electrodes i.e. RA, LA, and LL. This method of conducting an ECG is the least accurate as very little information can be gathered this way.
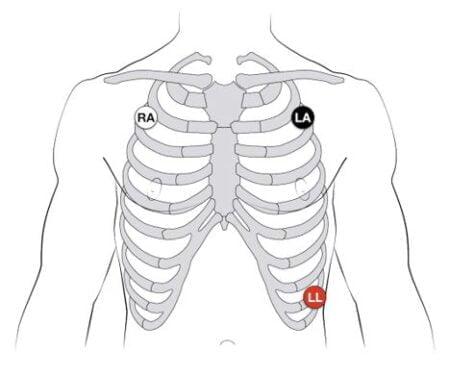
(Where RA=Right arm, LA=Left arm, and LL=Left leg)
How to place ECG electrodes?
Although conducting an ECG is a simple process, the correct placement of all the electrodes is a necessity. In the case of a 12-lead ECG, the electrode setting is most critical. Here are the steps to be followed for achieving the ideal electrode setting in order to get the best results:
- Preparation of the skin: Before starting the process, it is necessary to wipe the chest area properly using alcohol swabs. The purpose of this thorough cleaning is to wipe away any oil from the skin which may interfere with the signal measurement by the electrodes.
- Pick the spots for electrode placement on the chest: The next step is to decide and mark the points where the electrodes are to be attached. These points must include the following:
V1: 4th intercostal space to the right of the sternum
V2: 4th intercostal space to the left of the sternum
V3: Directly between the leads V2 and V4
V4: 5th intercostal space at midclavicular line
V5: Level with V4 at left anterior axillary line
V6: Level with V5 at midaxillary line
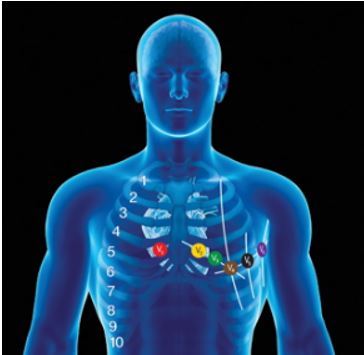
Points of electrode placement on the chest
- Pick the spots for electrode placement on the limbs: Once all the above-mentioned points are located and marked, put the electrodes in place. Moving forward, mark the rest of the points on the soft tissue of the limbs. These include:
RA: Upper right arm
LA: Upper left arm
RL: Lower right leg
LL: Lower left leg
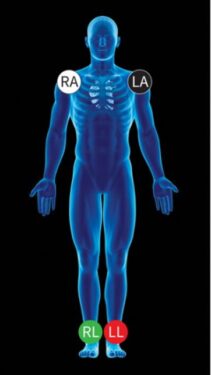
Points of electrode placement on the soft tissue of the limbs
- Connect the electrodes: Once all of the electrodes are put in place, connect the electrodes to the ECG machine via lead wires and record the signals.
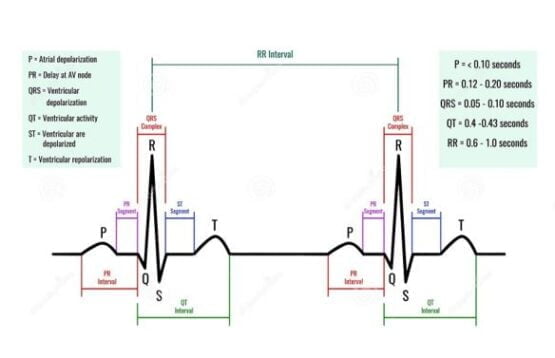
An electrocardiogram obtained after the test
Applications of ECG test
An ECG can be useful in the diagnosis of the following disease conditions among others:
- Arrhythmias i.e. abnormal heart rhythm
- Bradycardia i.e. low heart rate
- Tachycardia i.e. elevated heart rate
- Atrial fibrillation i.e. irregular heart rhythms due to the generation of abnormal electrical impulses
- Atrial flutter i.e. rapid pumping of the atria
- Heart block including both SA (sinoatrial node) block and AV (atrioventricular node) block
- Digitalis intoxication
- Serotonin toxicity
- Hypo or hypercalcemia i.e. low or high calcium levels
- Hypo or hyperkalemia i.e. low or high potassium levels
- Myocardial infarction i.e. heart attack
Conclusion
Among the frequently run laboratory tests to detect diseases or abnormalities in the body, ECG is of prime importance when it comes to testing the human heart. An ECG detects, transfers, and records the electrical signal of the heart which manifests the health of the cardiac tissue. This simple, non-invasive, reliable, rapid, and inexpensive test can easily portray the condition of a patient’s heart in the form of an electrocardiogram. Hence, this is one of the tests which has the physician’s approval.

PhD Scholar (Pharmaceutics), MPhil (Pharmaceutics), Pharm D, B. Sc.
Uzma Zafar is a dedicated and highly motivated pharmaceutical professional currently pursuing her PhD in Pharmaceutics at the Punjab University College of Pharmacy, University of the Punjab. With a comprehensive academic and research background, Uzma has consistently excelled in her studies, securing first division throughout her educational journey.
Uzma’s passion for the pharmaceutical field is evident from her active engagement during her Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) program, where she not only mastered industrial techniques and clinical case studies but also delved into marketing strategies and management skills.
Throughout her career, Uzma has actively contributed to the pharmaceutical sciences, with specific research on suspension formulation and Hepatitis C risk factors and side effects. Additionally, Uzma has lent her expertise to review and fact-check articles for the Health Supply 770 blog, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information presented.
As she continues her PhD, expected to complete in 2025, Uzma is eager to contribute further to the field by combining her deep knowledge of pharmaceutics with real-world applications to meet global professional standards and challenges.