Medical procedures, particularly surgeries, demand the utmost precision and meticulous attention. Even a minor oversight can lead to severe consequences, including fatalities. Among the intricate techniques employed by surgeons, one essential practice is warming blood prior to transfusion. blood warmers play a pivotal role in this process, given that blood is stored at cooler temperatures to maintain cell viability. Ensuring the blood reaches an optimal temperature before transfusion is vital for patient safety and treatment efficacy. In this article, we’ll look at why blood is warmed for transfusion and how this process is conducted:
How is blood warmed for transfusion?
Blood warmers or fluid warmers are medical devices that are used in hospitals and other medical settings to warm blood before transfusion.
A fluid warmer or blood warmer are fluid warming devices that are used to warm fluids including crystalloid, colloid, or blood products before administering to body temperature levels.
This helps to prevent hypothermia. These devices warm blood before transfusion and consequently help to avoid any undesirable consequences that may arise if cold blood is used for transfusion.
Warming blood before transfusion with the help of a blood warming system can help reduce the chances of hypothermia in surgical and physically traumatized patients and further lead to improved patient safety.
Disposable blood warmer
Reason for warming blood before transfusion
Warming blood before transfusion is an important part of the treatment of patients as it helps to avoid several complications as a result of cold blood transfusion. It can cause unnecessary suffering, prolonged duration of treatment, and hospital stay. Therefore it is necessary to warm blood before transfusion. Blood is warmed before transfusion for the following reasons:
Prevention of Hypothermia
One of the most important things that should be taken care of during surgeries is maintaining the patient’s core body temperature. It is necessary to prevent hypothermia which is a condition caused by being exposed to cold temperatures for a long period.
It can cause a person to lose consciousness and his pulse or breathing may become unnoticeable. Hypothermia can be fatal during surgery as it can cause complete failure of the heart and respiratory system. For this reason, blood given to the patient is warmed before transfusion.
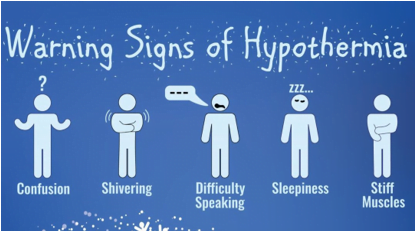
Signs of hypothermia
Cardiac arrest
Hypothermia can cause the body’s temperature to drop significantly and can result in complete cessation of cardio-pulmonary circulation. This can cause a cardiac arrest to occur and causes fifteen hundred deaths annually. Hypothermia can cause the heart to beat irregularly. Therefore to avoid cardiac arrest and to protect the heart from any potential damage from a cold blood transfusion, it is necessary to warm blood before transfusion into patients.
Slow heartbeat
Mild hypothermia can cause a person’s heartbeat to slow down. It can also cause abnormal heart rhythms that can sometimes be fatal. Therefore to reduce the chances of heart rate dysfunctions, blood should be warmed before transfusions.
Kidney failure
Hypothermia can affect the kidneys that can cause complete failure of the kidneys. Failure of kidneys can cause severe complications during the treatment and can even cause the death of the patient. Therefore it is highly significant to warm blood before transfusion to avoid hypothermia and other consequent complications.
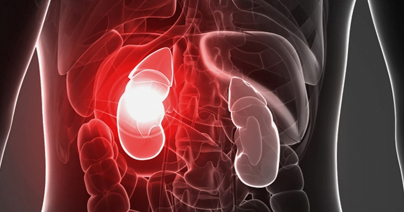
Kidney failure
Unconsciousness
Hypothermia can cause a person to lose consciousness and you may not be able to detect a person’s pulse or breathing. This can cause complications during the treatment. To avoid such undesirable conditions during the treatment, it is essential to warm blood before transfusion.
Bleeding disorders
Hypothermia can further lead to bleeding disorders that can become a threat to the safety of the patient. These bleeding disorders can cause the treatment to become difficult and may even cause severe complications. Therefore, to avoid the risk of bleeding disorders during the treatment, patients should always be provided with blood that has been warmed before transfusion.
Low respiratory rate
Hypothermia can cause a person’s breathing to become dangerously slow or to cease completely. This can cause complications during the treatment. Warming the blood before transfusion can help to avoid low respiratory rate in the patients.
Low blood pressure
In case of severe hypothermia, the blood pressure can drop and it can cause the patient to lose consciousness. To avoid low blood pressure during treatments or surgeries, it is important to provide blood to the patients that has been warmed before transfusion. Warming the blood appropriately can decrease the chances of a decline in blood pressure rates and consequently avoid complications.
Loss of muscle strength
Hypothermia can cause reduced strength in the muscles. It can cause the breakdown of muscle tissue. Therefore, in order to reduce the chances of the breakdown of the muscle tissue, blood must be warmed before transfusion.
Pulmonary edema
Severe hypothermia can lead to pulmonary edema which is a buildup of fluids in the lungs. This buildup can make it difficult for the patient to breathe. It can sometimes lead to the death of the patient. Therefore it should be avoided at all costs to ensure the safety of the patient. Warming the blood before transfusion can help to avoid pulmonary edema during treatment.
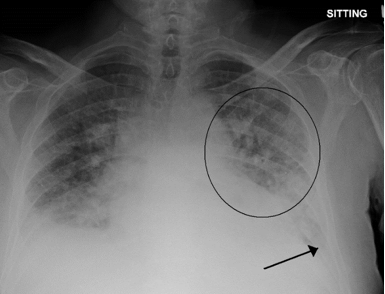
Pulmonary edema
Conclusion
Surgical or physically traumatized patients may need a blood transfusion during their treatment. This blood must be warmed using a blood-warming device before transfusion to ensure the patient’s safety. If blood is not warmed before transfusion, it can lead to hypothermia which can be mild, moderate, or severe.
According to the severity of hypothermia, the patient can suffer from some complications that can be life-threatening. Some of these complications include pulmonary edema, loss of muscle strength, low blood pressure and respiratory rate, unconsciousness, kidney failure, bleeding disorders, slow heart rate, and, even cardiac arrest. Some of these complications can lead to the death of the patient. Therefore to avoid these complications and ensure patient safety, it is important to warm blood before transfusion.

PhD Scholar (Pharmaceutics), MPhil (Pharmaceutics), Pharm D, B. Sc.
Uzma Zafar is a dedicated and highly motivated pharmaceutical professional currently pursuing her PhD in Pharmaceutics at the Punjab University College of Pharmacy, University of the Punjab. With a comprehensive academic and research background, Uzma has consistently excelled in her studies, securing first division throughout her educational journey.
Uzma’s passion for the pharmaceutical field is evident from her active engagement during her Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) program, where she not only mastered industrial techniques and clinical case studies but also delved into marketing strategies and management skills.
Throughout her career, Uzma has actively contributed to the pharmaceutical sciences, with specific research on suspension formulation and Hepatitis C risk factors and side effects. Additionally, Uzma has lent her expertise to review and fact-check articles for the Health Supply 770 blog, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information presented.
As she continues her PhD, expected to complete in 2025, Uzma is eager to contribute further to the field by combining her deep knowledge of pharmaceutics with real-world applications to meet global professional standards and challenges.