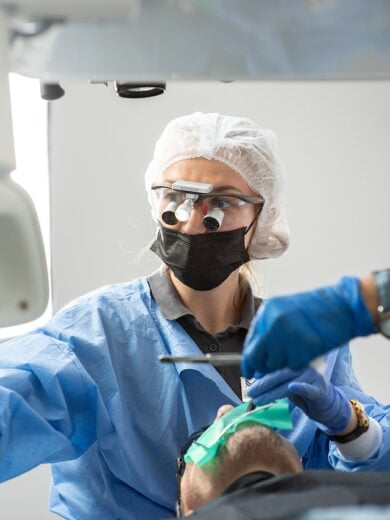
During a surgical procedure, it is very essential for the surgeon to see as clearly as possible. When the surgical area is properly focused with high-quality illumination, it becomes easy for medical professionals to visualize the internal damage and work accordingly. For this purpose, a surgical headlight is employed. These surgical headlights are durable as well as reliable surgical accessories that, despite being very light in weight, generate bright light. Let us look at the basic structure of a surgical headlight along with its applications.
What are surgical headlights?
Surgical headlights or portable headlamps are the user-controlled light sources employed by surgeons or other healthcare providers usually during invasive procedures. These are glare and reflection-proof and provide the appropriate amount of illumination for the procedure.
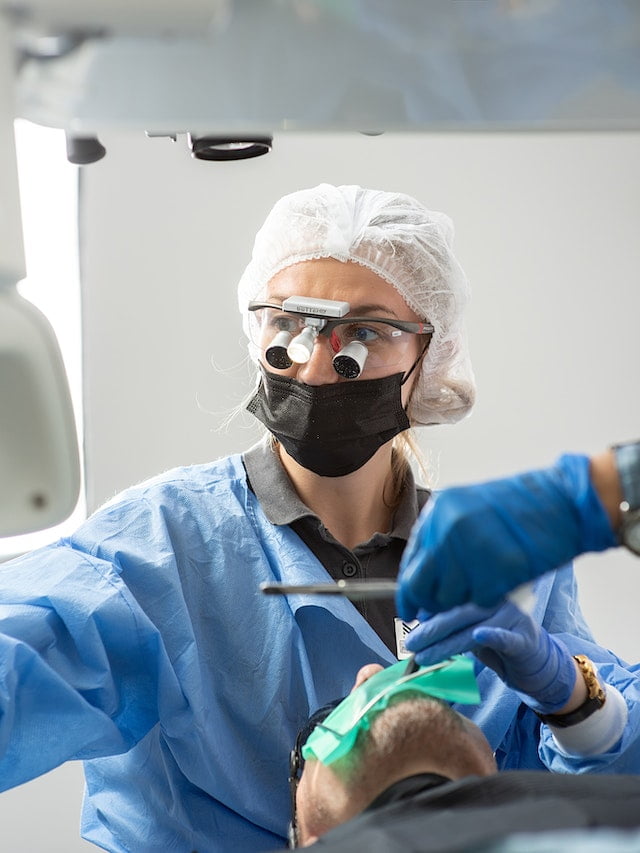
Surgical headlight being used during a medical procedure
-
Parts of a surgical headlight
A surgical headlight comprises the following parts:
- Adjustment of the light spot
- Screw for holding the lamp/light
- Screw for the adjustment of the height of the headband
- Knob for adjusting the girth of the headband
- Knob for controlling the brightness of the light
- Leather cushion acting as the base
- Batteries
- Charging hole
- On/off switch
-
Characteristic features of surgical headlights
The surgical headlights provide various benefits owing to their characteristic features enlisted below:
- Being lightweight, it is very easy to attach a surgical headlight to surgical glasses. They do not make the physician feel uncomfortable by putting too much pressure. Therefore, surgical headlights can be worn for hours during a longer medical procedure.
- Surgical headlights reduce the strain on the physician’s eyes by providing the appropriate amount of light needed for the procedure. If the light becomes too bright, it starts hindering the vision of its user thus reducing the visibility.
- These surgical headlights are portable and move with the surgeon. When properly placed, they automatically focus the area on which the surgeon wants to focus on.
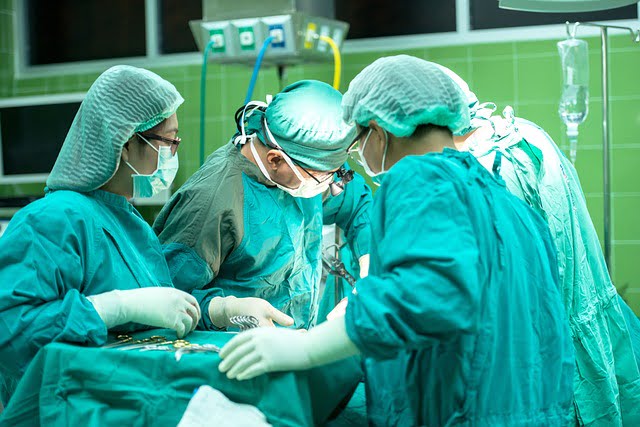
An invasive surgery being conducted with the employment of surgical headlights
- Surgical headlights, unlike overhead lights, do not cast shadows usually caused due to pendant light thus they do not impair visibility. Due to their positioning as well as the shadow control technology, the path of light coming from them is not hindered in any way thus providing maximum visibility with minimum usage issues.
- Surgical headlights affixed with CRI 95+ are able to make a distinction between the tissues. This is due to the color rendering index i.e. the capability of the light source to quantitatively measure and reveal the tissues differently.
- Some surgical headlights are also connected with a micro-camera with an aim to record the medical procedures being conducted and show them on the screen for the physicians and the nursing staff to observe.
Applications of surgical headlights
(a) Surgical headlamps, due to their versatility, find applications in the fields of:
- Medical surgery
- Dental procedures
- Veterinary processes
(b) With the use of a headlight, the physician is provided with the option of performing a procedure the way she or he thinks is best suited as the flexibility in the posture of the patient is enhanced.
Choosing the right headlight
As the procedures which are conducted with the help of surgical headlights vary, the need for light intensity as well as duration is also changed. For this purpose, a suitable headlight must be chosen prior to the conduction of a process. The things which must be kept in mind while making this decision include:
- Check which type of procedure is to be conducted with the headlight. Among these procedures, notable ones are:
– General office procedures
– Dental processes
– ENT
– Deep site surgery
– Deep tissue procedures, etc.
- Check how much brightness is needed for the procedure intended to be conducted based on the level of its invasiveness.
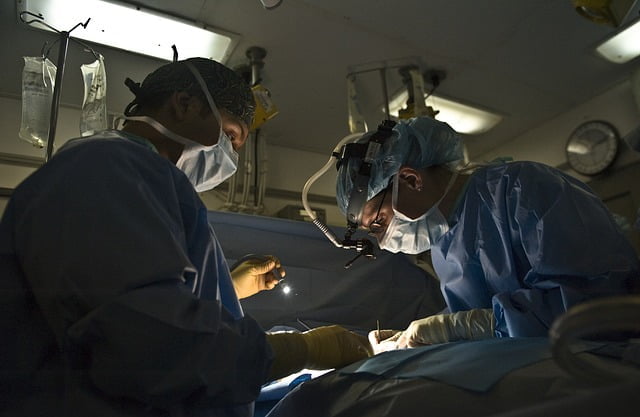
A surgical procedure being conducted with the help of surgical headlights
Cons of surgical headlights
Apart from their frequent use in different types of procedures, surgical headlights have some cons as well. One of the major issues among these is the eye strain that might be experienced by using headlights in a completely dark room. Addressing this issue, it has been recommended that surgical headlight must be used in conjunction with an overhead light to minimize the chances of eye strain.
Where to buy a surgical headlight?
Many companies associated with manufacturing medical instruments market surgical headlights. Some of these notable brands with good quality products include:
- Sunoptic Surgical
- Titan
- Zumax
- Welch Allyn
- Luxtec
- Ronin
- Karl Storz
- Dr. Kim
- Heine
- Integra
- Stryker
- Xenosys
- Napco
- ESC-ESC
- NSE
- Enova
- Lindkvist
- Kscope
- Richard Wolf
- QED Medical
- Pharos HD
- Day-Mark
- Bristol-Plus
- Dover
- High Bright Hatteras
- AtoN
- BayPort
Conclusion
The use of surgical headlights during various types of medical or dental procedures is a common practice by physicians. These lights provide concentrated bright light of appropriate intensity which only covers the intended area. Good-quality headlights restrict the sdow formation and facilitate the visualization of deep tissues distinctively. Thus, despite being a simple product, the advantages associated with a surgical headlight exceeds its limitations.

PhD Scholar (Pharmaceutics), MPhil (Pharmaceutics), Pharm D, B. Sc.
Uzma Zafar is a dedicated and highly motivated pharmaceutical professional currently pursuing her PhD in Pharmaceutics at the Punjab University College of Pharmacy, University of the Punjab. With a comprehensive academic and research background, Uzma has consistently excelled in her studies, securing first division throughout her educational journey.
Uzma’s passion for the pharmaceutical field is evident from her active engagement during her Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) program, where she not only mastered industrial techniques and clinical case studies but also delved into marketing strategies and management skills.