Just like the other body parts, the uterus is also prone to contracting infections and diseases which, although treatable in most cases, badly affect the quality of life of the individual. One of these issues is dysmenorrhea in which the person experiences moderate to severe period pain. An associated problem with dysmenorrhea is the decidual casting which is even more painful and extremely discomforting. Although it does not happen with every period as well as in every individual, decidual casting is a significant issue. Let us take a look at what decidual cast shedding is and how is it managed.
What is a decidual cast?
A decidual or uterine cast is the reddish or pinkish, fleshy uterine tissue that sheds from the uterus in a single piece or in the form of fragments via the vaginal route. It is dispatched from the endometrial layer of the uterus called decidua. Because of being in triangular uterus-like shape and placenta-like texture, it is easy to identify. This medical condition in which the decidua is shedding is called dysmenorrhea.
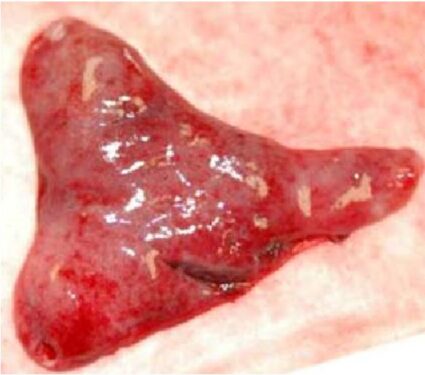
Decidual or uterine cast
Although a decidual cast is not an indication of the presence of a serious health issue in a non-pregnant individual, it is still advised to talk about it to your healthcare provider.
How big is a decidual cast?
Although the size of an upside-down pear-shaped decidual cast varies from person to person, it may be equal to the size of a person’s palm in most cases. However, it is hard to quantify the size of a uterine cast when it comes out in chunks instead of a unit.
Why does it happen?
It is tough to identify an exact reason for decidual casting but it can be owed to the following:
- An ectopic pregnancy i.e. a condition in which the zygote attaches with walls other than those of the uterus
- A miscarriage
- Presence of fibroepithelial polyps
- Tumors within the uterus known as sarcoma botryoides
- Presence of cancer of the soft tissue i.e. rhabdomyosarcoma
- Taking hormonal contraceptives which have a higher concentration of progesterone in the form of pills, injections, or implants
- Stoppage of contraceptives after a long time of use
- Taking HCG (human gonadotrophin) injections for the treatment of infertility
Symptoms of decidual cast
Before the discharge of a decidual cast out of the body, the following symptoms may be experienced:
- Discomfort and pain within the uterus
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- The feeling of extreme weakness and fainting

Pain with a decidual cast negatively impacts the quality of life
- Spotting from the vagina
- Heavy bleeding via the vaginal route
- Intense stomach and uterine muscle cramps
- Passage of large pieces of tissues from the uterus
These symptoms are short-lived and vanish as soon as the cast is excreted out of the body. However, if a group of conditions are affecting the uterus at the same time, the symptoms may persist thus generating the need for medical care.
Diagnosis of a decidual cast
A physician may start by taking your medical history to find out if you have ever experienced decidual casts before. A pregnancy test may be taken to rule out the possibility or, in another case, to confirm it. Diagnosing a decidual cast can be done based on the following examination methods:
- Symptomatic evaluation: Evaluation of the signs and symptoms experienced by the patient can help diagnose the decidual cast.
- Pelvic examination: Pelvic examination is done to check the severity of the issue.
- Pelvic imaging tests: Your doctor may advise you to take a pelvic imaging test in order to visualize the condition of the endometrium wall.

A patient consulting a physician
- Pelvic ultrasound: Pelvic ultrasound is another way to evaluate the exact condition of the pelvis.
- Laparoscopic evaluation: If the need arises, laparoscopy can also be done for the in-depth analysis of the uterine walls.
Are you at risk of a decidual cast?
If you are using hormonal contraceptives, this might increase your chances of experiencing a decidual cast. Even when the use is discontinued, the chances of the problem still remain. But the good news is that once you experience a decidual cast, it may be the first and the last time it happens. It is not a condition that continues to happen to a person and causes long-term health effects.
Is a decidual cast preventable?
No, it is not possible to prevent a decidual cast. However, if you are on birth control pills or any other hormonal therapy, it is advised to talk about the possibility of a decidual cast prior to its occurrence.
Does a decidual cast cause infertility?
No, according to the reported research, a decidual cast is not linked to infertility.
Decidual cast vs. miscarriage
A decidual cast differs from a miscarriage despite being identical in symptoms. Severe pain, cramping, bleeding via the vaginal route, as well as discharge of large pieces of tissues can be felt passing out of the uterus in both cases. If you are pregnant and then experiencing these symptoms, it is advised to immediately contact your gynecologist.
Conclusion
A decidual cast is one the rare yet significant uterine issues in which the passing of uterine lining during a period happens. An individual may experience a decidual cast every month or once in a lifetime as the condition is extremely rare to occur. Shedding and passing of a deciduous cast is painful but the pain ends once the shedding is complete. However, if the bleeding does not stop, one should immediately seek medical help.

PhD Scholar (Pharmaceutics), MPhil (Pharmaceutics), Pharm D, B. Sc.
Uzma Zafar is a dedicated and highly motivated pharmaceutical professional currently pursuing her PhD in Pharmaceutics at the Punjab University College of Pharmacy, University of the Punjab. With a comprehensive academic and research background, Uzma has consistently excelled in her studies, securing first division throughout her educational journey.
Uzma’s passion for the pharmaceutical field is evident from her active engagement during her Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) program, where she not only mastered industrial techniques and clinical case studies but also delved into marketing strategies and management skills.
Throughout her career, Uzma has actively contributed to the pharmaceutical sciences, with specific research on suspension formulation and Hepatitis C risk factors and side effects. Additionally, Uzma has lent her expertise to review and fact-check articles for the Health Supply 770 blog, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information presented.
As she continues her PhD, expected to complete in 2025, Uzma is eager to contribute further to the field by combining her deep knowledge of pharmaceutics with real-world applications to meet global professional standards and challenges.








