Since the beginning of time, humans have used several types of herbs and procedures to expedite wound healing. For this purpose, people in different parts of the world used several natural ingredients including honey, animal grease, herbs, leaves, and, various types of alcohol. This was done to stop the bleeding from the wound and to drain all the fluids from the wound. In this way, it helped to heal the wound faster and also in the prevention of an infection. The wounds caused by surgeries also need to be taken care of properly to ensure better wound management and save the patient from severe consequences including acute pain, swelling, and, infections.
What are wound drains?
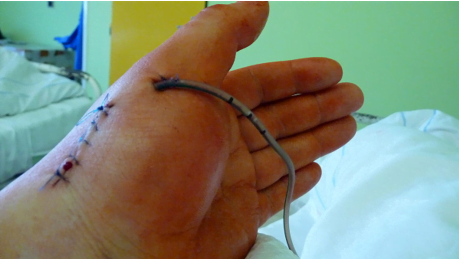
Wound drains
Some fluid can be collected in the surgical area after surgery. This fluid, if left collected inside the surgical site, can lead to infection. For this purpose surgical wound drains are used. These wound drains help to drain this fluid out of the surgical site where the fluid has been collected. Wound drains are used in several surgeries and for different kinds of wounds. These wound drains facilitate in draining of the fluid or air from the area of surgery. Wound drains are helpful in
- Preventing the accumulation of air (dead space).
- Preventing the collection of several fluids (pus, blood, and, infection-causing fluids).
- Characterizing the fluid.
To make sure that the wound heals faster, it is important to completely drain the wound of all these fluids or air. These wound drains are used in
- Chest drainage
- Infected cysts to drain pus
- Urinary catheters
- Nasogastric tubes
- Pancreatic surgery to drain secretions
- Thyroid surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Chest surgery
- Breast surgery to avoid the accumulation of lymph or blood
Types of wound drains
There are several types of wound drains. These types include open, closed, active, passive, silastic, or, rubber drains. Open drains drain fluids on a gauze pad or into a stoma bag while closed drains work by draining the fluids into a bottle or bag. The active drains are maintained under suction which can be high or low pressure while the passive drains do not include suction and work according to the differential pressure between body cavities and the exterior. Silastic drains induce minimal tissue reaction while rubber drains can induce an intense tissue reaction. Some of the most commonly used wound drains include the following.
Jackson-Pratt drain
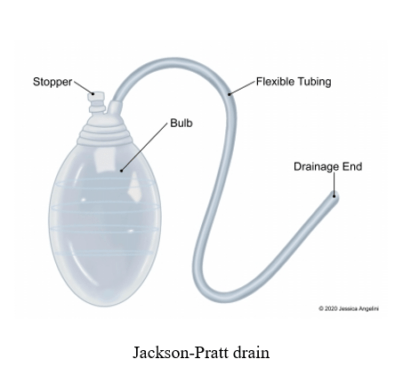
Jackson-Pratt drain
A Jackson-Pratt drain, also known as a JP drain, is a closed-suction device that helps to collect bodily fluids from surgical sites. It is commonly used as a post-operative drain. The JP drain includes an internal drain that is connected to a bulb. The flexible rubber tube is placed under or near the place of the incision and this tube helps to collect the fluids from the wound. A small bulb is connected to this rubber tube. This bulb also includes a stopper which helps to empty fluids and push air out. When the bulb is squeezed, it causes a suctioning effect. With the help of this suctioning procedure, fluids can be drawn out of the wound and into the bulb. The plug or stopper present on the bulb is used to drain the fluid that is collected by opening it and then it is again closed to re-engage the suction process. It is highly significant that the air must be squeezed out of the bulb every time it is emptied to keep pulling the fluid out of the wound.
Blake drain
This drain is made up of silicon and is used after open-heart surgeries to remove excess fluid around the lungs. It helps the patients to recover fast. The Blake drain uses a vacuum system that helps to draw fluids from the wound into a reservoir bulb. The vacuum of the bulb must be maintained always to help in drainage and prevent blockage. This drain should be emptied when there is no vacuum in the bottle.
Penrose drain
A Penrose drain is a flat, flexible, and soft tube that is made of latex. This tube is used to drain fluids from the surgical site or wound. This can help to remove the collection of fluids from the wound and prevent infection. A part of the drain is inserted into the body. The ends of the drain come out from the area of the incision. The blood or fluid from the wound is drained on a dressing. A small tab is used at the end of the drain which helps to keep the drain in its place. The duration for which the drain is placed depends upon the type of surgery and the amount of fluid that is to be removed. It is removed when no fluid drains out of the wound.
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT)
The NPWT is a method that is used to prevent infection by draining the fluids out of the wound. This procedure works with the help of a special dressing, tubing, a negative pressure device, and, a canister to collect fluids. The dressing is sealed with a file and a tube is attached to it. This tube helps to collect the fluid or blood from the wound. The fluid is collected using a vacuum pump and it also helps to pull the edges of the wound together.
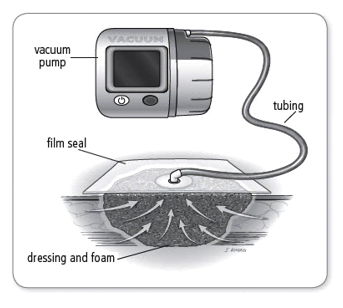
Negative pressure wound therapy
Conclusion
Wound drains are extremely helpful medical devices that are used to drain fluids (blood, pus, or air) out of the wounds and prevent infection. These drains are an important part of wound management and care as they help to drain the infection-causing fluids out of the wound and help avoid severe consequences caused by these fluids. These wound drains can be open or closed, active or passive, and, rubber or silastic and can be used according to the requirement of patient. Several types of wound drains are used and the selection of a wound drain depends upon the type of surgery and also the area of the body for which the drain will be used. Due to the assistance wound drains provide in preventing infection and expediting wound healing, these drains have become an important part of wound care.

PhD Scholar (Pharmaceutics), MPhil (Pharmaceutics), Pharm D, B. Sc.
Uzma Zafar is a dedicated and highly motivated pharmaceutical professional currently pursuing her PhD in Pharmaceutics at the Punjab University College of Pharmacy, University of the Punjab. With a comprehensive academic and research background, Uzma has consistently excelled in her studies, securing first division throughout her educational journey.
Uzma’s passion for the pharmaceutical field is evident from her active engagement during her Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) program, where she not only mastered industrial techniques and clinical case studies but also delved into marketing strategies and management skills.
Throughout her career, Uzma has actively contributed to the pharmaceutical sciences, with specific research on suspension formulation and Hepatitis C risk factors and side effects. Additionally, Uzma has lent her expertise to review and fact-check articles for the Health Supply 770 blog, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information presented.
As she continues her PhD, expected to complete in 2025, Uzma is eager to contribute further to the field by combining her deep knowledge of pharmaceutics with real-world applications to meet global professional standards and challenges.








