Use of the Harmonic Scalpel vs Conventional Knot Tying for Vessel Ligation in Thyroid Surgery
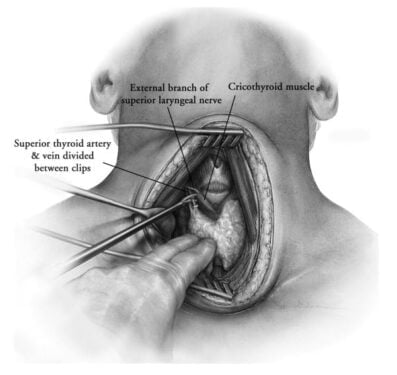
In recent years, the number of patients with thyroid complications such as lobectomy, neck dissections, para-thyroidectomy, subtotal, total, or completion thyroidectomy has risen. Consequently, the health system is bearing increased patient pressure many of whom require thyroid surgery at some point. Many conventional as well as the latest methods are being employed in these surgeries to improve the overall physician as well as patient experience. Therefore, a comparison can be made among these methods in terms of their efficiency and convenience.
Let us briefly discuss the methods first to draw a just comparison.
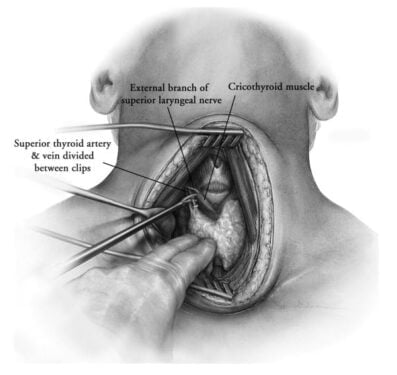
Thyroid surgery is under process
Conventional methods of tissue ligation
The conventional methods of vessel ligation during thyroid surgery include:
- Hand tying of the two ends of a vessel before division
- Monopolar electrocautery: In this method, two electrodes are placed on the patient’s skin. An active electrode directs the current toward the target tissue followed by exiting the body via a return electrode.
- Bipolar electrocautery: In bipolar cautery, two electrodes are put near the target tissue. The current only passes between these two electrodes.
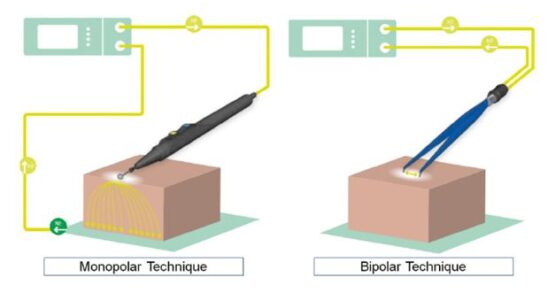
A comparison of monopolar and bipolar techniques
- Lasers ablation: The employment of percutaneous laser ablation for the removal of thyroid tissue is a minimally invasive surgical technique.
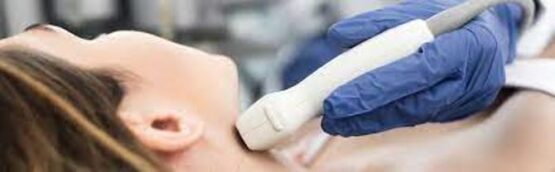
Laser ablation treatment of the thyroid gland
- Surgical clips: Clips can be used to hold the tissue together for a brief period of time after thyroidectomy. These clips are to be removed after a few weeks after the procedure.
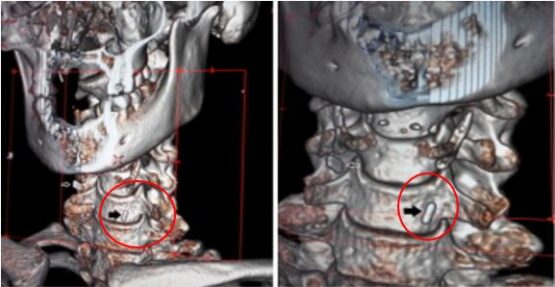
Surgical clips visible in a patient’s neck
- The use of staples: Staples can be used at the surgical site for 5 to 7 days to hold the tissue together.
Disadvantages of the conventional vessel ligation techniques
Although each of these methods has been in use for centuries, they all come with certain disadvantages:
- With monopolar and bipolar electrocautery, an angle change during the surgical procedure is limited.
- The employment of laser technology enhances the chances of an injury to the target tissue as well as to the nearby tissues during the process.
- The clips, when used at a target site, are easy to get dislodged thus rendering the process difficult. Blood loss may also enhance in this case. Moreover, they are also suitable for larger vessels only.
- The staples get wasted thus their use is costly during surgery.
Harmonic scalpel
A harmonic scalpel, abbreviated as HS, is the latest vessel cutting and cauterization system which works on the principle of ultrasonic frictional heating i.e. conversion of ultrasonic waves into mechanical energy. For this purpose, high-frequency ultrasonic waves i.e. frequency not exceeding 55.5 kHz or 55,500 vibrations/second is required.

A Harmonic scalpel with its active or vibrating jaw and inactive or straight jaw visible
Working with a Harmonic scalpel
When the dissection is conducted by using a Harmonic scalpel, it is termed ‘Ultracision’. A Harmonic scalpel performs its job in the following steps:
- Ultrasonic energy is provided to the Harmonic scalpel which is converted into mechanical energy. The temperature of the area does not exceed 80°C.
- As, due to lower temperature, the water in the tissues is not subjected to boiling, the proteoglycans and collagen protein in the tissue get mixed up with this intracellular as well as interstitial fluid.
- This combination results in the formation of a jelly-like substance called coagulum.
- The mechanical energy provided by the Harmonic scalpel degenerates the coagulum protein present in a vessel resulting in the fusion of vascular tissue.
Advantages of Harmonic scalpel
The Harmonic scalpel has the following added advantages to its easy and safer use:
- The Harmonic scalpel uses ultrasonic energy instead of electrical energy.
- It can cut through vascular tissue while its proteins are being coagulated.
- The surgery usually takes an average of 184.2 minutes which is lesser as compared to conventional methods.
- The thermal spread is less than 1 mm.
- Blood loss during and after the surgery is insignificant.
- Tissue sticking with the device during the surgery is minimum.
- The length of the incised skin at the target tissue is minimum.
Comparison of conventional tissue ligation methods with Harmonic scalpel
A comparison can be drawn between the efficacy of the conventional tissue ligation approaches and the Harmonic scalpel which is given below:
- As the Harmonic scalpel works at a temperature lower than the boiling point of water i.e. 80°C, the heat thus generated does not degenerate the nearby tissues. Hence the injury is less than 1.5 mm.
- The employment of a Harmonic scalpel also cuts the operation time by 30 minutes. This time efficiency also renders a reduced demand for anesthesia.
- Post-operative recovery time is lessened with the use of a Harmonic scalpel.
- When the use of conventional methods was compared with the use of a Harmonic scalpel, the latter was found to cause fewer post-operative complications.
- The cost of both procedures is comparable.
Conclusion
With the rise in thyroid disorders in the past decade, the need has arisen to improve the methods of treatment and surgery. In the wake of this, both conventional as well as latest methods are being implemented for thyroidectomy. If a comparison is drawn between the conventional techniques and a relatively latest method i.e. Harmonic scalpel, the latter depicts a prominent superiority above the prior ones in terms of the operation time, incision length, level of injury as well as cost. Thus, the Harmonic scalpel can be termed a dominant method for conducting thyroid surgeries.