What are the Benefits of External Ventricular Drains?
Multiplicity exists in the conditions which may result in an enhanced concentration of cerebrospinal fluid within the cerebral ventricles. This higher-than-usual concentration of brain fluid results in increased intracranial pressure (ICP) which may further induce certain complications. Therefore, the physician’s first choice when it comes to treating this state is the employment of methods through which a reduction in ICP is possible. Although the road to the development of a successful method, in this regard, was not an easy one but all the efforts have bore fruit as the external ventricular drain system is working efficiently to achieve the required aims. Let us take a look at what this external ventricular system is and what benefits it has to provide.
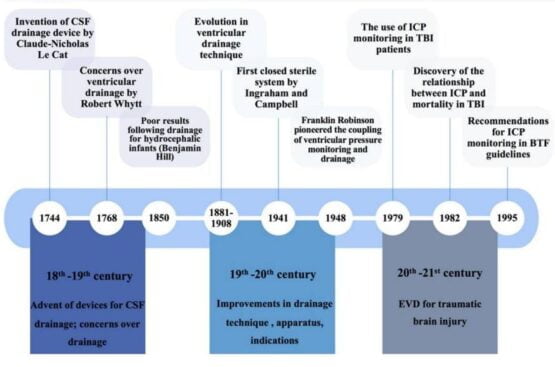
A brief history of the development of ventricular drainage procedure
What are external ventricular drains?
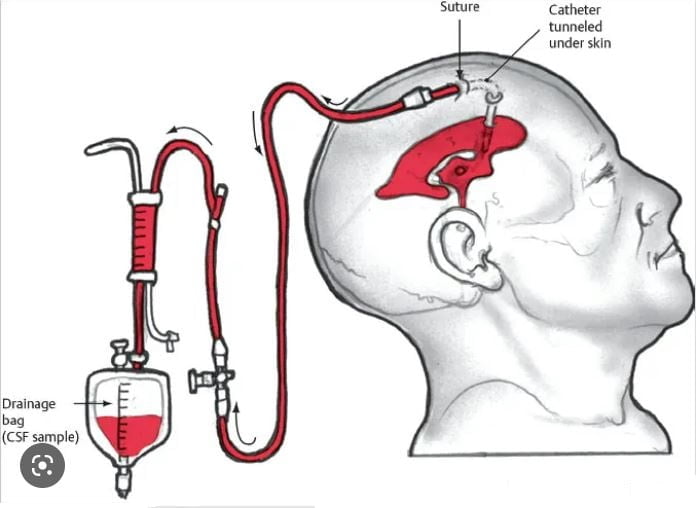
An external ventricular drainage system or EVD, also known as ventriculostomy, is a neurosurgical procedure employed to reduce the pressure of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the brain. It is done by connecting the external drainage system with the cerebral ventricles.
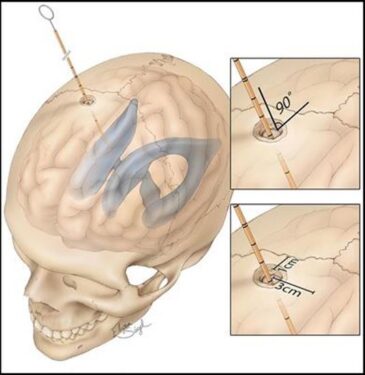
EVD inserted into the cerebral ventricles
Components of an external ventricular drain
An external ventricular drain consists of the following parts:
- A pressure scale that indicates the amount of drainage
- A pressure transducer
- A drip chamber
- The catheter along with its tubing connects the EVD with the collection system
- Collection system, affixed with a collection bad, to contain the drained fluid
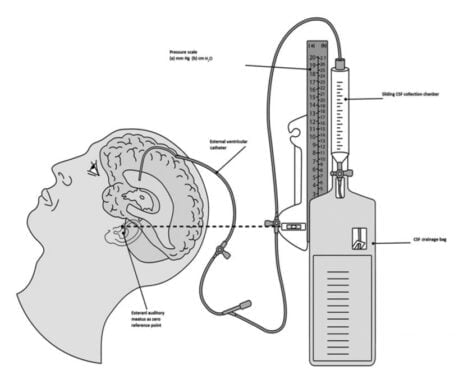
Components of an EVD system
Placement of an external ventricular drain
The placement of an external ventricular drain inside the cerebral ventricles is done in the following steps:
- The ideal point of an EVD placement is the frontal horn of the right lateral ventricle, a place near the Foramen of Monro.
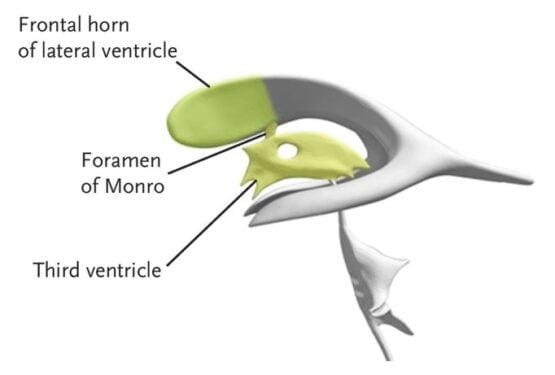
Ideal point of EVD insertion
- Once the position has been located, the patient’s head is maintained at 30°C and the EVD is inserted carefully under sterile conditions and the incision site is secured with staples or sutures.
- As soon as the placement is complete, the EVD catheter is connected to the external drainage system consisting of a collecting machine affixed with a collection bag.
- A measuring chamber is attached to the drainage bag in order to quantify the level of drainage.
- For the rest of the time period, the drainage system is maintained at its vertical position to ensure smooth flow. For this purpose, the drainage system is secure with a drip stand.
- Once a drainage bag is filled up to 75%, it must be changed immediately with another one, if necessary.
Benefits of external ventricular drainage system
The external ventricular drainage system has the following implementations in the field of medical science:
- The external ventricular drainage system has been beneficial for the management of traumatic brain injury (TBI) during which the elevated CSF pressure is problematic. The employment of EVD can help reduce this ventricular pressure thus preventing further brain damage.
- The drainage system is also useful for clearing up the CSF infected with pathogens. This happens in the case of a cerebral infection when the infectious material spreads into the CSF and then runs with it throughout the central nervous system. As a treatment, it is recommended to drain out the CSF-containing pathogenic entities and pump antibiotics directly into the ventricles.
- External ventricular drainage is also utilized prior to brain surgery with the aim to reduce intracranial pressure (ICP).
- Acute symptomatic hydrocephalus, a condition characterized by the abnormal buildup of CSF in the cerebral ventricles mostly in old age, is also treated by the employment of an external ventricular drain.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is one of the situations where the EVD is employed, again for the purpose of reducing ICP.
- Additionally, in the case of intraventricular bleeding termed intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), EVD is also utilized to clear out the accumulated blood.
- In some cases, an EVD can be employed instead of a lumbar drain with the aim to facilitate brain relaxation during surgery.
Risks associated with EVD system
External ventricular drain, despite its vast applications, is a technique with more than one associated risk and side effects which are enlisted as follows:
- Although the EVD technique is itself used to empty the brain of infectious material, it can sometimes become the cause of transferring an infection into the body. The rate of these infections, in fact, is very high i.e. exceeding 20%. Therefore, sterile practices must be adopted before inserting the EVD tube into the cerebral ventricles.
- As EVD is an invasive process, it can damage the insertion passage while its employment may result in bleeding. In such cases, the immediate intervention of a neurosurgeon is required as the condition may become life-threatening. Bleeding becomes even more dangerous if the patient has a history of coagulopathy i.e. bleeding disorder.
- Despite being an extremely rare case, there exists a possibility of EVD seeping too deeply into the brain. This may cause irritation to the cerebral components other than the ventricles and may result in different kinds of complications.
Conclusion
One of the most frequently used methods of reducing the ICP is the employment of external ventricular drains, abbreviated as EVD. This technique provides an easy, quick, and economical way of draining the excess cerebrospinal fluid out of the brain thus acting as a life-saving aid in certain health conditions. The EVD, although comes with fewer but pronounced side effects, is still considered a life-saving device in neuroscience owing to its vast applications.