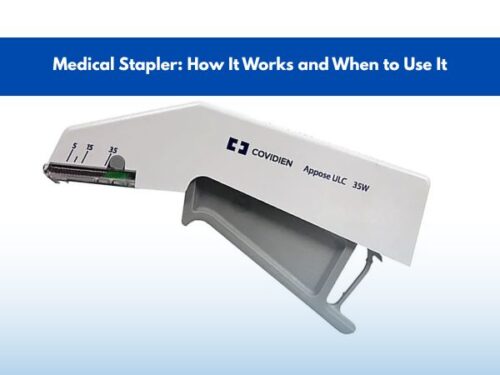
Medical Stapler: How It Works and When to Use It
Proper wound closure is fundamental to surgical success and faster patient recovery. While suturing has been the traditional standard, modern medical staplers offer a faster, more efficient alternative that reduces operative time and improves outcomes across multiple surgical disciplines.
Medical staplers have become indispensable in contemporary surgery—from emergency trauma care to complex gastrointestinal procedures. This comprehensive guide explains how surgical staplers work, their applications across specialties, and why hospitals and surgical centers are increasingly choosing staplers over traditional suturing methods.
What Are Medical Staplers?
Medical staplers are specialized surgical instruments designed to secure tissue edges and create reliable wound closure through mechanical fastening. Unlike manual suturing, which requires precise hand movements and significant operative time, medical staplers deliver consistent, automated closure in seconds.
These devices deploy biocompatible staples (made from stainless steel, titanium, or absorbable materials) that compress tissue edges together, creating a secure seal that promotes healing. Staplers are used for internal tissue approximation, external skin closure, and creating anastomoses (surgical connections between two structures) across all major surgical specialties.
Key advantages of surgical staplers:
- Reduce operative time by 30-40% compared to suturing
- Lower infection rates in controlled studies
- Provide consistent compression without manual variation
- Enable rapid closure in trauma and emergency situations
- Minimize tissue trauma with precise, uniform staple placement
- Work effectively in high-tension wound areas (abdomen, scalp, back)
How Do Medical Staplers Work? Step-by-Step Process
Understanding stapler mechanics helps surgical teams maximize safety and effectiveness. Here’s how the firing process works:
Step 1: Select the Appropriate Stapler Type
The first critical decision is choosing the right device for the tissue type and surgical site. Medical staplers come in multiple configurations:
- Linear staplers: Deliver staples in a straight line; ideal for GI, gynecological, and general surgery
- Circular staplers: Create a circular staple pattern; essential for anastomoses in colorectal and gastric surgery
- Endoscopic staplers: Designed for minimally invasive surgery; pass through trocar cannulas
- Skin staplers: Applied externally; fire one staple at a time for skin edge approximation
- Specialty staplers: Vascular, thoracic, or articulating variants for complex procedures
Device selection also considers tissue thickness, wound tension, and surgical application. A surgeon must match stapler characteristics to anatomical requirements.
Step 2: Position the Stapler Properly
Correct positioning is essential for achieving secure closure:
- The stapler is placed perpendicular to the wound or tissue edges
- Tissue is evenly compressed between the anvil and cartridge jaws
- Pressure is applied to bring edges together uniformly
- The device is held steady without excessive force that could cause tissue damage
Proper alignment ensures staples penetrate tissue at consistent depth, creating uniform compression. Misalignment can result in incomplete staple formation or tissue trauma.
Step 3: Fire the Staples
Once positioned correctly, the surgeon activates the firing mechanism:
- The trigger or handle is pressed (single-hand operation on most modern staplers)
- The device fires staples in sequence, advancing automatically
- An audible click and tactile feedback confirm each staple deployment
- The surgeon can pause and reposition between fires or perform continuous stapling, depending on the device and procedure
Most surgical staplers can deliver 6-15 staples per reload, with automatic advancement to the next staple position after each firing.
Step 4: Inspect and Complete Closure
After stapling is complete:
- The surgeon visually inspects all staples to confirm proper placement
- Staple line integrity is verified—no gaps or incomplete staples
- Additional staples can be placed if needed for optimal approximation
- The device is carefully removed to avoid disrupting the staple line
Staple materials matter: Modern surgical staples are made from:
- Stainless steel: Most common; excellent tissue compatibility; requires removal
- Titanium: Superior biocompatibility; ideal for patients with metal sensitivities
- Absorbable materials: Dissolve in the body over 60-90 days; eliminates removal procedures (often used in gynecological and abdominal closure)
Types of Surgical Staplers Explained
External/Skin Staplers
Used for closing skin wounds and superficial lacerations:
- Fire single staples at a time for precise placement
- Ideal for scalp, face, trunk, and extremity wounds
- Commonly used in emergency departments for trauma
- Disposable designs reduce infection risk
- Staples typically removed 7-10 days post-operatively
Clinical advantage: Skin staplers reduce time spent in emergency settings, allowing faster patient discharge and improved ED throughput.
Internal Staplers
Designed for deep tissue approximation inside the body:
Linear staplers (most common):
- Deploy staples in a single line across the tissue
- Used in gastrointestinal, gynecological, and general surgery
- Create either open or closed staple patterns depending on the cartridge
- Reload cartridges come in various staple heights (2.0-4.8mm) to match tissue thickness
Circular staplers:
- Create a circular staple pattern for end-to-end or end-to-side anastomoses
- Essential in colorectal surgery, bariatric surgery, and esophageal procedures
- Ensure watertight seals in GI reconstruction
- Reduce anastomotic leak rates compared to hand-sewn closures
Endoscopic staplers:
- Designed for minimally invasive procedures
- Pass through small trocar cannulas (5-12mm)
- Include articulating heads for angled stapling in tight spaces
- Enable same-day discharge with reduced postoperative pain
Uses of Medical Staplers Across Surgical Specialties
General Surgery
Surgeons use staplers for:
- Skin closure: Rapid approximation of incision edges on high-tension areas (abdomen, back, chest)
- Bowel resection: Anastomosis of small and large intestine during cancer treatment, obstruction relief, or inflammatory bowel disease surgery
- Trauma care: Rapid closure during emergency procedures, preventing contamination of traumatic wounds
- Tissue approximation: Securing organs and soft tissues during resection procedures
Outcome advantage: Studies show surgical staplers reduce operative time by 30-40% in abdominal procedures compared to hand-sewn closures, while maintaining or improving healing outcomes.
Gastrointestinal Surgery
GI procedures represent the largest application area for surgical staplers:
- Gastric surgery: Bariatric procedures (gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy) rely heavily on staplers for rapid, reliable closure of gastric tissue
- Bowel anastomosis: Reconnecting intestine after resection (cancer removal, Crohn’s disease, obstruction)
- Esophageal procedures: Creating anastomoses in esophageal cancer or achalasia surgery
- Liver surgery: Securing hepatic tissue edges during partial hepatectomy
Clinical benefit: Circular staplers in GI surgery create watertight seals that significantly reduce leak rates—a serious complication in abdominal surgery.
Gynecological Surgery
Gynecological applications have expanded significantly:
- Hysterectomy: Stapling uterine vessels and tissue to reduce blood loss
- Cervical closure: Securing the vaginal cuff after hysterectomy to prevent prolapse
- C-section closure: Absorbable staples close the uterine incision, eliminating the need for suture removal
- Endometrial cancer surgery: Sealing vaginal cuff with endoscopic staplers reduces tumor cell spillage into the pelvis
Surgical advantage: Absorbable staples in gynecological closures reduce patient anxiety about post-operative visits and eliminate suture-related complications.
Cardiothoracic Surgery
Thoracic surgeons use staplers for:
- Lung resection: Securing lung tissue during partial or complete lobectomy
- Pulmonary artery/vein ligation: Creating airtight seals on major vessels
- Bronchial closure: Preventing bronchopleural fistula—a serious complication post-lung surgery
- Cardiac procedures: Vascular anastomoses in coronary artery bypass grafting
Critical advantage: Surgical staplers create consistent, airtight seals in lung surgery that reduce the incidence of air leaks and bronchopleural fistula, major sources of morbidity.
Trauma and Emergency Care
In high-volume trauma settings, speed is survival:
- Scalp lacerations: Rapid closure of head wounds in conscious patients
- Trunk wounds: Quick approximation of torso injuries
- Extremity lacerations: Closure of limb injuries without extensive operative time
- Hemorrhage control: Tissue compression reduces bleeding during emergency procedures
Emergency medicine advantage: Surgical staplers enable rapid closure, reducing operative time in unstable patients and improving survival in hemorrhagic shock scenarios.
Vascular Surgery
Vascular staplers ensure precise, leak-free vessel anastomoses:
- Arterial reconstruction: Creating vein or synthetic graft anastomoses
- Carotid surgery: Precise closure in carotid endarterectomy
- Peripheral vascular procedures: Femoral, tibial, and other peripheral vessel repairs
Precision advantage: Vascular staplers provide superior precision compared to hand-sewn techniques, reducing thrombosis and leak rates.
Comparison: Surgical Staplers vs. Traditional Suturing
Operative Time
- Staplers: 5-10 minutes for most closures
- Sutures: 20-40 minutes (varies by complexity)
- Advantage: Staplers reduce operative time by 70-80%
Infection Rates
- Staplers: 2-4% in controlled studies
- Sutures: 3-6% depending on procedure type
- Advantage: Comparable or superior outcomes with staplers
Patient Outcomes
- Staplers: Faster healing, consistent compression, reduced tissue inflammation
- Sutures: Traditional approach; surgeon-dependent variations in tension
- Advantage: Stapler consistency improves predictable healing
Cost Considerations
- Staplers: Higher device cost ($50-300 per stapler)
- Sutures: Lower material cost ($5-20)
- Real-world consideration: Operative time savings offset device cost in hospital settings
Stapler Safety and Proper Technique
Pre-operative Safety Checks
Before using any surgical stapler:
- Verify device functionality (test fire if applicable)
- Confirm staple cartridge compatibility with stapler model
- Check expiration dates on sterile staple cartridges
- Inspect for visible damage or defects
- Ensure safety mechanisms are intact
Firing Technique Best Practices
- Maintain steady pressure: Avoid excessive compression that damages tissue
- Allow complete staple formation: Wait for the audible click before removing the stapler
- Avoid misfires: If incomplete stapling occurs, reposition and re-fire rather than applying excessive force
- Monitor anastomotic integrity: Visually inspect the staple line after each section
Recognizing and Addressing Problems
Misfires or incomplete staples: Indicates tissue too thick or stapler malfunction; reposition and attempt again or switch to thicker-cartridge stapler
Excessive bleeding: Apply gentle pressure or reinforcing sutures; never force additional staples into an already-stapled line
Jamming: Remove stapler carefully; clear any tissue fragments; do not force the trigger
Staple line gaps: Reposition and add staples to close any visible separations
Post-operative Staple Management and Removal
When to Remove Staples
Typical timelines vary by location:
- Scalp/face: 7-10 days
- Trunk: 10-14 days
- Extremities: 10-14 days
- Abdominal surgery: 14+ days or per surgeon direction
Absorbable staples don’t require removal—they dissolve in 60-90 days.
Staple Removal Procedure
- Special staple remover instruments are used (not standard scissors)
- The instrument lifts each staple from beneath
- Gentle pressure releases the staple from tissue
- The process is quick but may cause minor discomfort
Post-removal Wound Care
- Apply antibiotic ointment to staple puncture sites
- Avoid submersion in water for 24 hours after removal
- Monitor for signs of infection (redness, drainage, warmth)
- Scar maturation continues for 12-18 months
Medical Stapler Selection: What to Consider
When choosing surgical staplers for your facility:
Clinical Factors
- Procedure type: Different surgeries require different stapler configurations
- Surgeon preference: Familiarity improves outcomes
- Patient factors: Allergy considerations (titanium vs. steel), healing capacity
- Specialty requirements: Endoscopic, vascular, or specialty staplers
Operational Factors
- Single-use vs. reusable: Cost per use vs. sterilization requirements
- Inventory management: Supply chain, expiration dates, storage
- Training requirements: Staff competency with specific devices
- Support and service: Manufacturer technical support availability
Economic Factors
- Device cost: Ranges from $50-300 per stapler
- Reload cartridge cost: $30-150 per reload
- Total cost of ownership: Including sterilization or disposal costs
- Surgeon volume: High-volume surgeons justify investment in specialized devices
Featured Medical Staplers at Health Supply 770
At Health Supply 770, we stock leading surgical stapler brands trusted by surgical teams across the United States. Our medical professionals can help you select the right device for your procedures.
ETHICON TX30G – Precision Surgical Stapler
Best for: General surgery, gastric procedures, gynecological applications
The ETHICON TX30G is renowned for versatility and reliability across multiple surgical specialties. Its lightweight design reduces surgeon fatigue during extended procedures, while compatibility with standard ETHICON reloads simplifies inventory management.
Key features:
- Reloadable design for cost-effectiveness
- Compatible with standard ETHICON cartridges
- Optimal tissue compression (no tissue over-compression)
- Ideal for surgeons needing a multi-specialty stapler
Shop ETHICON TX30G → [ETHICON TX30G – Precision Surgical Stapler]
ETHICON GST45G – Premium Precision Surgical Stapler
Best for: Thoracic surgery, gastric procedures, bariatric surgery
The GST45G is a maxi articulating stapler specifically designed for complex procedures requiring precision and control. Single-hand operation improves surgeon freedom, while the 45mm staple line length accommodates thick tissue.
Key features:
- 12 staples per cartridge
- Single-hand firing capability
- Articulating design for hard-to-reach areas
- Ideal for bariatric and thoracic applications
Shop ETHICON GST45G → [ETHICON GST45G – Premium Precision Surgical Stapler]
ConMed 803590 Reflex Regular One Skin Stapler
Best for: Emergency departments, trauma centers, skin closure
The ConMed Reflex is purpose-built for rapid skin closure in high-volume settings. Its ergonomic design and visible staple counter make it ideal for busy emergency departments managing high-strain wounds.
Key features:
- Single-use disposable (no sterilization needed)
- 35 stainless steel staples per device
- Ergonomic grip reduces hand fatigue
- Visible staple counter shows remaining capacity
- Audible click confirms staple placement
Shop ConMed Reflex → [ConMed 803590 Reflex Regular One Skin Stapler]
COVIDIEN EGIA45AVM – Premium Endoscopic Stapler with Tri-Staple Technology
Best for: Minimally invasive surgery, bariatric procedures, GI surgery
The COVIDIEN endoscopic stapler is engineered for precision in confined surgical spaces. Tri-Staple technology ensures superior grip and seal integrity, while the compact design passes easily through standard trocar cannulas.
Key features:
- Compatible with standard 5-12mm trocar cannulas
- Tri-Staple technology for enhanced security
- Adjustable stapling for variable tissue thickness
- Maximum visibility and maneuverability in tight spaces
Shop COVIDIEN EGIA45AVM → [COVIDIEN EGIA45AVM – Premium Endoscopic Stapler with Tri-Staple Technology]
Choosing Between Stapler Types: A Quick Reference
| Procedure Type | Recommended Stapler | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Scalp/skin lacerations | Skin stapler (single-use) | Speed and ease of removal |
| Bowel resection & anastomosis | Linear or circular stapler | Tissue thickness and leak prevention |
| Bariatric surgery | Articulating stapler (GST45G style) | Access and precision in difficult areas |
| Minimally invasive surgery | Endoscopic stapler | Size and maneuverability |
| Vascular procedures | Precision stapler (circular preferred) | Consistent seal integrity |
| Gynecological procedures | Absorbable stapler preferred | Eliminates post-op staple removal |
| Emergency trauma | Rapid-deployment skin stapler | Speed over complexity |
Stapler Maintenance and Sterilization (Reusable Devices)
For reusable surgical staplers:
Cleaning
- Wipe external surfaces with sterile gauze immediately after use
- Use enzymatic cleaner for any tissue residue
- Rinse with sterile water
- Never soak entire device; keep electronics dry
Sterilization
- Steam sterilization (autoclave) at 250°F for 3-4 minutes
- Flash sterilization protocols acceptable for reusable devices
- Follow manufacturer-specific instructions for your stapler model
- Validate sterilization indicators before use
Maintenance Checks
- Inspect firing mechanism quarterly
- Test functionality before each surgical session
- Replace worn grips or damaged cosmetic parts
- Service per manufacturer recommendations
Common Questions About Medical Staplers
Q: Are staplers safe for all patients?
A: Yes, with appropriate device selection. Titanium staplers work for patients with steel sensitivity; absorbable staplers eliminate removal concerns.
Q: How long does staple removal take?
A: Typically 5-10 minutes for most wounds. It’s a quick office procedure.
Q: Can staplers be used in infected wounds?
A: Generally no. Wounds must be clean and free of infection before stapling.
Q: Do patients prefer staplers or stitches?
A: Most patients find staple removal easier and faster than suture removal. Healing outcomes are comparable.
Q: What’s the learning curve for using a new stapler model?
A: Minimal for experienced surgeons. A few practice fires are usually sufficient. OR staff benefit from manufacturer training.
Conclusion
Medical staplers represent a significant advancement in surgical wound closure, reducing operative time while maintaining or improving healing outcomes. From emergency trauma care to complex gastrointestinal procedures, surgical staplers have become indispensable across all surgical specialties.
Whether your facility needs rapid skin closure in high-volume emergency settings, precision closure in minimally invasive procedures, or reliable approximation in complex gastrointestinal surgery, selecting the right stapler impacts both patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Health Supply 770 provides access to the leading surgical stapler brands trusted by surgeons worldwide. Our medical equipment specialists can help you identify the best devices for your facility’s specific needs and patient population.
Ready to upgrade your OR’s wound closure capabilities? Browse our complete selection of surgical staplers and medical supplies. [CTA: Shop Surgical Staplers] or [CTA: Contact our medical equipment specialists for personalized recommendations]
Additional Resources
For more information on surgical techniques and medical devices:
- [“Top-Rated Skin Stapler Devices for 2025: Surgeon’s Choice“]
- [“Different Types of Stapler Used in Surgical Procedures“]
- [“Stapler Use in the Operating Room: Safety and Technique Guide“]
About the Author
Uzma Zafar, PharmD is a clinical pharmacist specializing in surgical supply selection and healthcare facility operations. With extensive experience in medical device evaluation and procurement, Uzma provides evidence-based guidance on surgical instruments and medical equipment. Her expertise helps healthcare facilities optimize clinical outcomes while managing operational costs.
Questions or need personalized recommendations? Contact Health Supply 770’s medical equipment specialists at [770-874-0431] or visit our [About Us page].