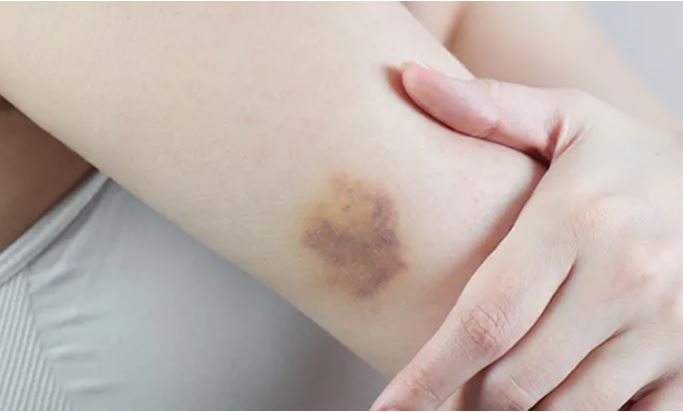
The human skin, our largest organ, not only covers the body in order to protect the internal structures but also signals if anything goes wrong inside it. By noticing a change in the color or texture of the skin, many health issues can be primarily identified. Similarly, the skin expresses bruises, hematomas, or other colored painful spots which appear on it due to varying reasons. But what is the difference between a hematoma and a bruise? How to differentiate them? Once identified, how should I give primary care? This article answers many of these frequently asked questions regarding hematomas as well as bruises. So let’s dive in.
What is a hematoma?
A hematoma is the extravascular accumulation of blood under the skin due to the bursting of a blood vessel. This results in bulging or inflammation at the target site.
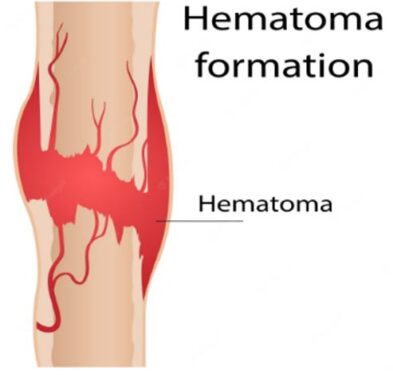
A hematoma formed due to the pooling of blood out of a blood vessel
Causes of a hematoma
The common causes of hematoma formation in the body include:
- Presence of aneurysms
- Bone-related injuries
- Use of certain medicines
- Presence of viral infections in the body such as chickenpox, mumps, rubella, HIV, or hepatitis C
- Recent phlebotomy i.e. puncturing of blood vessel with the aim to draw blood or administer a fluid or a drug
- Presence of a disease e.g. leukemia
Symptoms of hematoma
Now if you are thinking, ‘What does a hematoma look like?’ here is the answer. The following are the symptoms of a hematoma which help to identify them:
- Redness as well as tenderness of the skin
- Pain and inflammation
- The feeling of warmth at the affected site
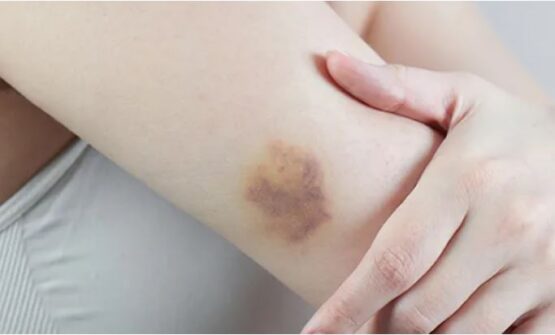
A patch of skin affected by a hematoma
How to diagnose a hematoma?
For the diagnosis of a hematoma, your physician might first look at your symptoms which can give away a soft tissue hematoma. However, if there is an indication of a severe hematoma, then any of the following tests can be recommended for confirmation:
- CT scan
- X-rays
- Ultrasound
- MRI
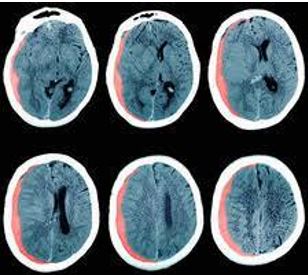
Hematoma within the skull detected by CT scan
How to treat a hematoma?
For the treatment of a hematoma, simple home remedies and some rest can indeed work like magic. These include putting ice cubes on the affected area and self-medicating with painkillers such as Tylenol or Advil. Painful hematoma can be managed by practicing the RICE method which includes:
- Rest and protect the affected site
- Ice or a cold pack which is to be put onto the hematoma
- Compression was applied to the affected area by wrapping the site
- Elevating or supporting the injured site
However, if the hematoma does not subside by doing these, it is best to consult your physician.
Are you at risk of hematoma formation?
Individuals with any of the following are more prone to hematoma formation than others:
- Progressing age
- Traumatic experiences in the recent past
- Use of blood thinning medications i.e. anticoagulants
What is a bruise?
A bruise, often termed a contusion, is a painful outgrowth on the skin which is formed as a result of the microscopic rupture of the blood vessels due to a recent trauma or an injury.
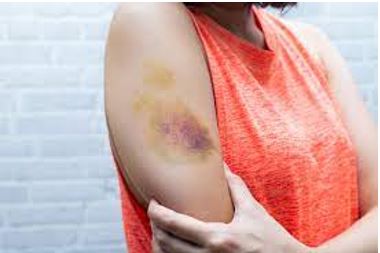
Skin affected by bruising
Causes of a bruise
The following may be the causes of bruising in the body:
- Bumps or accidents
- Tearing of the blood vessels adjacent to the skin
- Thinning of the skin due to old age
- Bleeding disorders
Symptoms of bruising
The appearance of the following may indicate the presence of a bruise:
- Purplish or bluish appearance of the skin at the affected area
- Pain and tenderness around the affected site
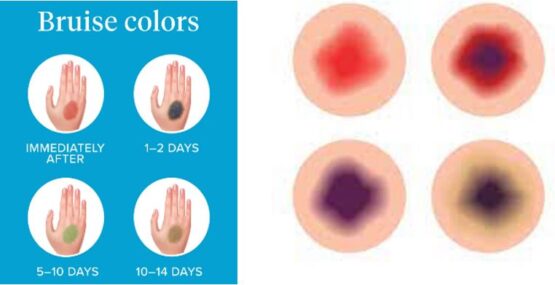
Changing the colors of a bruise over time
Diagnosis of a bruise
The diagnosis of a bruise is easy as compared to a hematoma because the individual can self-identify the changes in the skin texture and color. If it is severe, then it is advised to consult a physician who might want to go for an X-ray. However, if the bruising is frequent, it is better to run some tests to rule out the possibility of a bleeding disorder or, in another case, to confirm it.
How to treat a bruise?
A hematoma and a bruise, however different, can be treated by similar methods. The employment of the RICE method is also recommended in case of a bruise.
Are you at risk of bruising?
If you have any of the following health conditions, you may be at risk of experiencing bruising:
- Prolonged vitamin C deficiency
- Presence of bleeding disorders
- Use of anticoagulants
Hematoma vs bruise
| Parameters | Hematoma | Bruise |
| Definition | A collection of blood in the area of an injury | An injury to small blood vessels |
| Common causes | Bone fracture, rupturing of a blood vessel due to a needle, injury due to impact | Hitting an object |
| Symptoms | Pain, inflammation | The red bruise turning purple and then yellow |
| Diagnosis | Painful swollen areas can be diagnosed by CT scan, MRI, X-rays, etc. | Color change in the affected area |
| Risk factors | Old age, trauma, anticoagulant use | Vitamin C deficiency, bleeding disorders, anticoagulant use |
| Treatment | RICE method, surgery if the hematoma is in the brain | Often not required. Ice can help with the pain |
Conclusion
A hematoma, like a bruise, is a modification in the color and texture of a skin patch. Although both occur due to different reasons, it is possible to identify them and provide primary care at home. In most cases, this initial care is enough to get rid of a hematoma or a bruise but if not effective, it is advised to consult a physician for proper therapy.

PhD Scholar (Pharmaceutics), MPhil (Pharmaceutics), Pharm D, B. Sc.
Uzma Zafar is a dedicated and highly motivated pharmaceutical professional currently pursuing her PhD in Pharmaceutics at the Punjab University College of Pharmacy, University of the Punjab. With a comprehensive academic and research background, Uzma has consistently excelled in her studies, securing first division throughout her educational journey.
Uzma’s passion for the pharmaceutical field is evident from her active engagement during her Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) program, where she not only mastered industrial techniques and clinical case studies but also delved into marketing strategies and management skills.
Throughout her career, Uzma has actively contributed to the pharmaceutical sciences, with specific research on suspension formulation and Hepatitis C risk factors and side effects. Additionally, Uzma has lent her expertise to review and fact-check articles for the Health Supply 770 blog, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information presented.
As she continues her PhD, expected to complete in 2025, Uzma is eager to contribute further to the field by combining her deep knowledge of pharmaceutics with real-world applications to meet global professional standards and challenges.