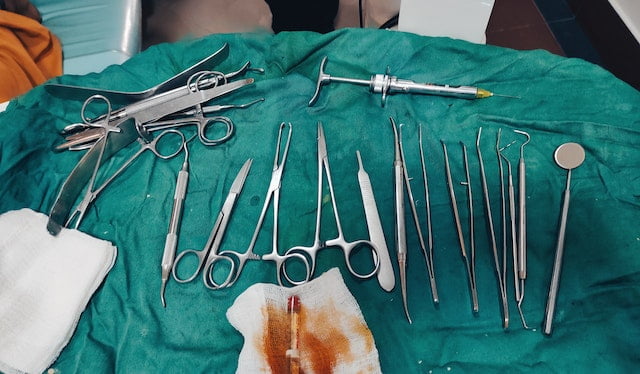
During surgical interventions, closing up a wound after the surgery is a clinical practice that is performed on a daily basis in healthcare setups. To do so, multiple options are available which include the use of adhesive strips, fibrin glue, suturing, etc Although all of these methods have their advantages and limitations, newer options are still being designed and manufactured. One such device is the surgical stapler which is not only time-efficient but also provides reliable performance. Let us take a look at what these surgical staplers are and in which surgeries they are usually used.
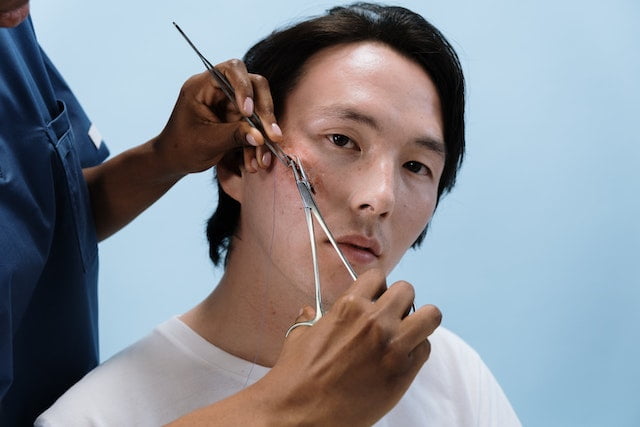

What are surgical staplers?
Surgical staplers are devices, made up of stainless steel, titanium, polyactide-polyglycolide copolymer, or plastic, which are employed to close the wounds or incised tissues during surgery. The staples fed up in the device are disposable and can be easily applied as well as removed once their job is done.
The device is designed in a way that it can insert multiple staples at a time. These surgical staplers have been proven to be an effective replacement for conventional methods such as suturing or stitching the skin up after an invasive procedure.
Types of surgical staplers
Surgical staplers, based on their shape and conformation, come in two types. Both reusable as well as disposable options are available in these types of surgical staplers. These involve:
· Circular staplers:
Circular staplers are best suited for the surgeries of the digestive tract. Owing to the circular layout, these can easily attach two sections of tube-like structures forming donut-shaped pinched tissue between the staples.
· Linear staplers:
Linear staplers are often employed during minimally invasive surgeries. Once the staples are in place, the surgeon usually waits for at least 30 seconds to ensure that there is an absence of bleeding or detachment.
How do surgical staplers work?
A surgical stapler, when employed on a tissue, works by inwardly compressing the cellular structure with the help of multiple B-shaped surgical staples. As a result, the wound is closed often with the removal of extra tissue.
Surgical staplers, along with many other kinds of medical devices, are available at great prices at Health Supply 770. Do check them out for making a purchase.
Advantages of surgical staplers
Surgical staplers are given preference over other means of stitching up the skin or internal tissues due to the following advantages this technique has over other methods:
·.
· Conventional stitching methods cause more pain to the patient at the time of conduction as well as afterward. However, with the use of surgical staplers, pain is lesser and the patient’s comfort is enhanced.
· Surgical staplers are also suitable to conduct minimally invasive surgeries as well as they can be inserted into the body via a small opening followed by cutting and sealing of the tissues as well as blood vessels. Moreover, the method also easily works when employed in areas with lesser muscle mass.
Applications of surgical staplers
Surgical staplers find vast applications in the field of medical procedures due to their prominent characteristics which aid recovery and save time. Some of these applications have been summarized below:
·://hs770.com/product/919363pillow-case-tissue-blue-cs100/” data-wpil-monitor-id=”11526″>tissue are some of the advantages achieved in this case.
·;
·!– /wp:paragraph –>
· A tingling sensation in the tissue followed by a feeling of cold
· Extreme pain sometimes accompanied by high-grade fever
· The presence of yellow or green pus in the tissue with foul-smell
· Bleeding at the site of surgery
Conclusion
Reconnecting the skin tissue after incision is essential during surgery. For this purpose, many conventional methods have been used which include suturing or taping the area. These methods, although extremely useful, come with a lot of demerits like the longer recovery time, extreme pain, and frequent infections.
Stapling the incised area or internal body tissue is a relatively novel technique that has solved many issues commonly experienced with suturing. However, the chances of acquiring an infection with staplers seem higher, the method is still superior to others owing to its various advantages and applications.
·!– /wp:paragraph –>
·!– /wp:paragraph –>
· Vertical banded gastroplasty surgery or stomach stapling is a technique to control an individual’s weight. For this purpose, a surgical stapler is employed.
Use of surgical staples and the risk of infections
A study published in Arthroplasty in the year 2022 compared the incidence rate of acquiring an infection after suturing as well as after the use of surgical staplers in elective knee and hip arthroplasties.
The findings of the investigation revealed a significantly higher chance of the stapled site getting infected as compared to the one in which suturing was involved. This may be attributed to the material used in the staples which does not dissolve like the sutures do thus accumulating microbes which result in an infection. Thus, it becomes essential to look for any signs of infection at the site of surgery.
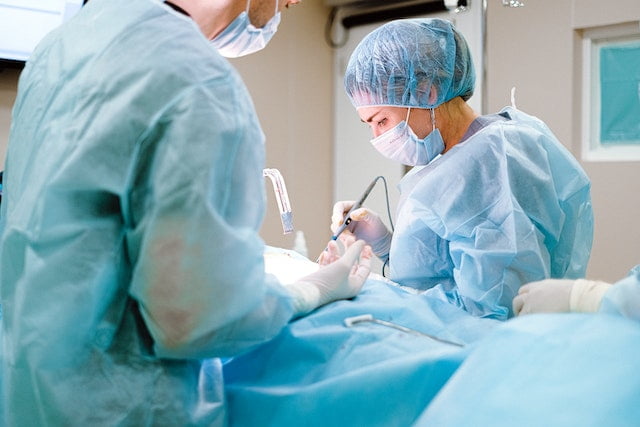
Other risks associated with surgical staplers
In addition to the high risk of infections, one should immediately refer to a healthcare professional if any issue is observed at the site where surgical staples have been applied. You may need additional care and further procedures if the stapled area shows any of the following signs:
·!– /wp:paragraph –>
· A tingling sensation in the tissue followed by a feeling of cold
· Extreme pain sometimes accompanied by high-grade fever
· The presence of yellow or green pus in the tissue with foul-smell
· Bleeding at the site of surgery
Conclusion
Reconnecting the skin tissue after incision is essential during surgery. For this purpose, many conventional methods have been used which include suturing or taping the area. These methods, although extremely useful, come with a lot of demerits like the longer recovery time, extreme pain, and frequent infections.
Stapling the incised area or internal body tissue is a relatively novel technique that has solved many issues commonly experienced with suturing. However, the chances of acquiring an infection with staplers seem higher, the method is still superior to others owing to its various advantages and applications.
·!– /wp:paragraph –>
·!– /wp:paragraph –>
· Vertical banded gastroplasty surgery or stomach stapling is a technique to control an individual’s weight. For this purpose, a surgical stapler is employed.
Use of surgical staples and the risk of infections
A study published in Arthroplasty in the year 2022 compared the incidence rate of acquiring an infection after suturing as well as after the use of surgical staplers in elective knee and hip arthroplasties.
The findings of the investigation revealed a significantly higher chance of the stapled site getting infected as compared to the one in which suturing was involved. This may be attributed to the material used in the staples which does not dissolve like the sutures do thus accumulating microbes which result in an infection. Thus, it becomes essential to look for any signs of infection at the site of surgery.

Other risks associated with surgical staplers
In addition to the high risk of infections, one should immediately refer to a healthcare professional if any issue is observed at the site where surgical staples have been applied. You may need additional care and further procedures if the stapled area shows any of the following signs:
·!– /wp:paragraph –>
· A tingling sensation in the tissue followed by a feeling of cold
· Extreme pain sometimes accompanied by high-grade fever
· The presence of yellow or green pus in the tissue with foul-smell
· Bleeding at the site of surgery
Conclusion
Reconnecting the skin tissue after incision is essential during surgery. For this purpose, many conventional methods have been used which include suturing or taping the area. These methods, although extremely useful, come with a lot of demerits like the longer recovery time, extreme pain, and frequent infections.
Stapling the incised area or internal body tissue is a relatively novel technique that has solved many issues commonly experienced with suturing. However, the chances of acquiring an infection with staplers seem higher, the method is still superior to others owing to its various advantages and applications.

PhD Scholar (Pharmaceutics), MPhil (Pharmaceutics), Pharm D, B. Sc.
Uzma Zafar is a dedicated and highly motivated pharmaceutical professional currently pursuing her PhD in Pharmaceutics at the Punjab University College of Pharmacy, University of the Punjab. With a comprehensive academic and research background, Uzma has consistently excelled in her studies, securing first division throughout her educational journey.
Uzma’s passion for the pharmaceutical field is evident from her active engagement during her Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D) program, where she not only mastered industrial techniques and clinical case studies but also delved into marketing strategies and management skills.
Throughout her career, Uzma has actively contributed to the pharmaceutical sciences, with specific research on suspension formulation and Hepatitis C risk factors and side effects. Additionally, Uzma has lent her expertise to review and fact-check articles for the Health Supply 770 blog, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the information presented.
As she continues her PhD, expected to complete in 2025, Uzma is eager to contribute further to the field by combining her deep knowledge of pharmaceutics with real-world applications to meet global professional standards and challenges.