What Is Pneumonia? Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments

What Is Pneumonia?
Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly 1.4 million people living in the United States suffered from pneumonia in 2021. Among them, approximately 42,000 patients did not survive the disease which accounts for nearly 12 deaths per 100,000 people. Considering the morbid effects of the disease, it is good to know the common causes and symptoms of pneumonia. These can not only help you to prevent yourself from the disease but also give a basic understanding of when to see a doctor if you experience any of the associated symptoms of pneumonia.

Pneumonia can cause excessive coughing and chest pain
In this article, let us learn what exactly pneumonia is, what causes it, and what are the associated symptoms. In addition, we will also look into the available treatment options for the disease.
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs which can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It is characterized by the inflammation of the air sacs called alveoli. As a result, the alveoli are filled with pus and become unable to exchange gases through their surface. If both lungs are affected, the condition is referred to as double pneumonia.
In this condition, the patients cough a lot. In most cases, pneumonia is treatable without causing any permanent damage to the lungs. However, in some people such as infants or the elderly, the disease can also become life-threatening.
Causes
Pneumonia happens when the germs responsible for the disease enter your lungs and cause an infection. As a result, the patient’s weakened immune system becomes activated and tries to combat the infection by attacking the causative agent. This immune response causes the alveoli to get inflamed and pus or other fluids start to fill them. The major types of pneumonia based on the causative agents include the following:
Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial infection is caused by several bacterial entities which include:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Legionella pneumophila
- Haemophilus influenza
Is pneumonia contagious?
Yes, when pneumonia is caused by bacteria or viruses, it is contagious and can be transferred from one person to another. This majorly happens due to inhaling the airborne droplets that are generated when a patient coughs or sneezes. However, fungal pneumonia does not spread from person to person.
Viral Pneumonia
Sometimes, the cause of pneumonia is not bacterial. Rather, the disease is caused by viruses. These viruses first cause a viral infection which then progresses to cause bacterial pneumonia. Although viral pneumonia is milder in symptoms as compared to bacterial one, it can still initiate the latter. Some of these viral entities include the following:
- Influenza or flu virus
- Rhinoviruses (common cold viruses)
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
- Viruses responsible for measles
- Varicella-zoster virus (responsible for chickenpox)
The infections that usually progress to cause pneumonia include:
- Adenovirus infection
- Coronavirus infection
- SARS-CoV-2 infection
- HMPV or human metapneumovirus infection
- HPIV or human parainfluenza infection
Fungal Pneumonia
When it comes to fungal pneumonia, it is important to remember that the fungal spores that we inhale from soil or the fecal matter of birds are responsible for causing the disease. Some of the commonly known pneumonia-causing fungi are:
- Pneumocystis jirovecii
- Histoplasmosis species
- Cryptococcus species
- Coccidioides species
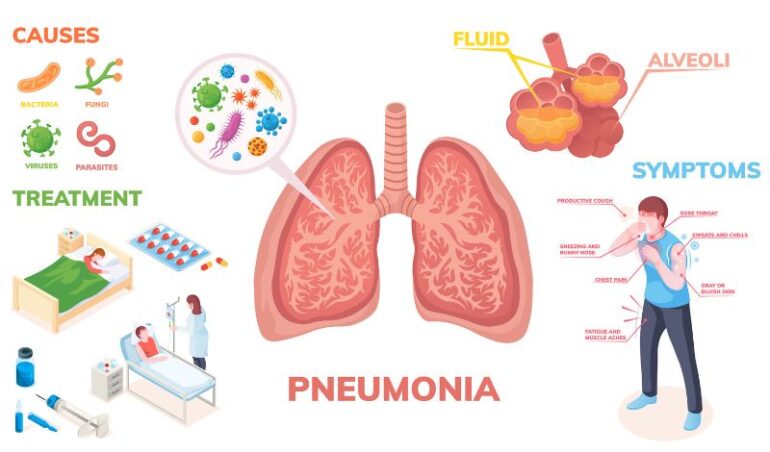
Causes and symptoms of pneumonia
Symptoms
The following serious symptoms have been associated with pneumonia:
- Cough during which phlegm or mucus is discharged
- Fever (Usually 102°F or 39°C)
- Chills
- Sweating
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing (especially in children)
- Stabbing chest pain, especially during coughing
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea with abdominal pain
- Fatigue or extreme tiredness
- Loss of appetite
- Headache
- Fast pulse
- Bluish appearance of lips and fingernails
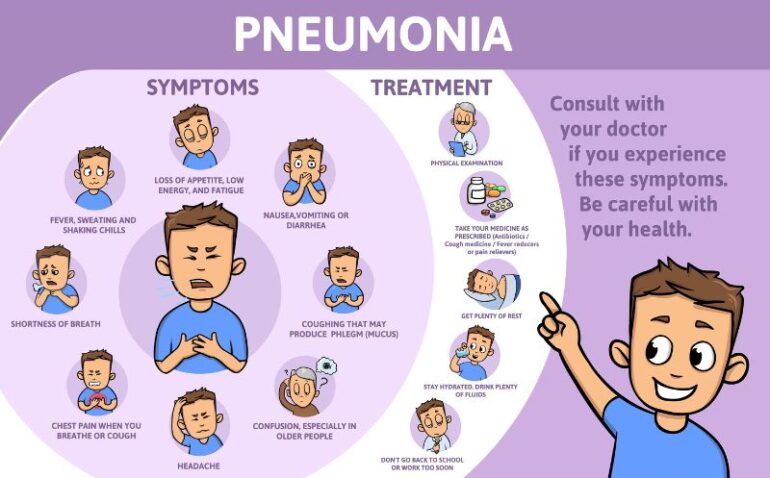
Symptoms and treatment options for pneumonia
Occurrence of Pneumonia: High-Risk Group
People who are more likely to contract pneumonia usually have the following risk factors:
- Infants up to 2 years of age
- Individuals aged 65 or above
- Immunocompromised individuals (i.e. who have a weakened immune system)
- Pregnant women
- HIV-positive individuals or AIDS patients
- People on medications such as anticancer drugs or steroids
- Smokers
People with certain medical conditions such as:
- Asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Heart failure
- Diabetes
- Cystic fibrosis
- Liver issues
- Kidney disease
- Sickle cell anemia
- Stroke
- Dementia
- Head trauma
- Parkinson’s disease
In addition, exposure to air pollutants or toxic fumes also elevates the risk of getting pneumonia.
How to Diagnose Pneumonia?
To diagnose pneumonia, the given steps are followed:
Medical History
The first thing your doctor will do is to take your medical history. This helps give away the symptoms you might have due to the presence of pneumonia in your lungs.
Physical Examination
During physical examination, your doctor will check you with a stethoscope. If abnormal sounds can be heard from your lungs, it might indicate the presence of pneumonia.
Pulse Oximetry
A pulse oximeter can also help detect pneumonia. As an oximeter checks the level of oxygen in your blood, it can indirectly indicate if your lungs are properly working or not. A value between 95 to 100% is considered normal and shows that your lungs are expanding properly. If your oximeter is displaying a number lower than this range, your doctor might want to conduct other tests to confirm pneumonia.
Chest X-ray
Taking an X-ray of the chest area helps the physician to check if swelling is visible in your lungs. In addition, it is also possible to locate the exact site of inflammation.

Physical examination is the first step in diagnosing pneumonia
Blood Culture Test
Taking a blood sample and culturing it can confirm pneumonia as well as its causative agent.
Sputum Culture Test
Sputum, also known as phlegm, is the thick mucus that is present throughout our air passageway. When we cough, this sputum sometimes gets out of the respiratory tract. In the case of taking a sputum culture test, a sputum sample is collected after the patient coughs deeply. This is then cultured and checked for the presence of certain bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
Fluid Sampling
Apart from the sputum analysis, a fluid sample can also be taken directly from the lungs. For this purpose, a needle is inserted between your ribs, and fluid is collected. This not only confirms the presence of disease but also its causative agent.
Computed Topography or CT Scan
A picture of the lungs taken from a CT scan can also show their exact condition.
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is an invasive test in which a guided camera is passed through your respiratory tract. This allows the doctor to see the inner linings of your throat and also get a clear picture of your lungs.
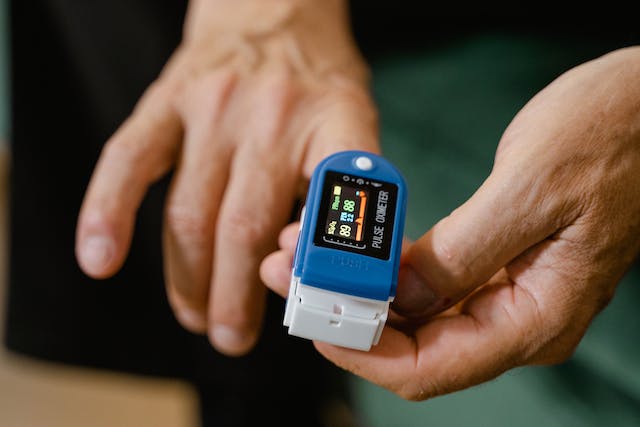
A pulse oximeter can also indicate the presence of bacterial and viral pneumonia
Treatment Options
Once the presence of viral and bacterial pneumonia is confirmed, the next step is to treat the disease. For this purpose, the following options are recommended:
Home-Based Remedies
Home-based remedies cannot fully heal your lungs if you have pneumonia. However, these can provide assistance and help relieve some of the associated symptoms. For instance, cough can be controlled in the following ways:
- Drinking warm water with honey
- Taking peppermint tea
- Gargling with saltwater
Medications
Antibiotics
Based on the type of causative agent, pneumonia patients can be prescribed certain medications. These include oral antibiotics which can be useful if the infection is bacterial. In case of the viral nature of the infection, antibiotics do not work. Rather, home-based remedies along with the use of assistive medications for fever and body pain are recommended.
If the causative agent is fungi, then antifungal medications are needed. The duration of therapy depends upon the severity of your condition. Therefore, medications should be taken as long as your doctor advises.
Over-the-counter (OTC) Medications
OTC medications such as aspirin, acetaminophen (Tylenol), as well as ibuprofen (Advil) are also required in case of pneumonia. This is because body pain, chest pain, headaches, as well as fever are often associated with the infection. Therefore, to give the patient some relief until the infection is fully cleared, OTC drugs are prescribed.
Hospitalization
If your infection is severe and the symptoms are not going away even after taking antibiotics, your doctor might want you to be hospitalized. This way, you can receive oxygen therapy which helps with poor oxygenation of the body.
In addition, antibiotics can be administered intravenously which reach the target area faster. The doctor might also want to conduct more tests and then change the dosage regimen accordingly.
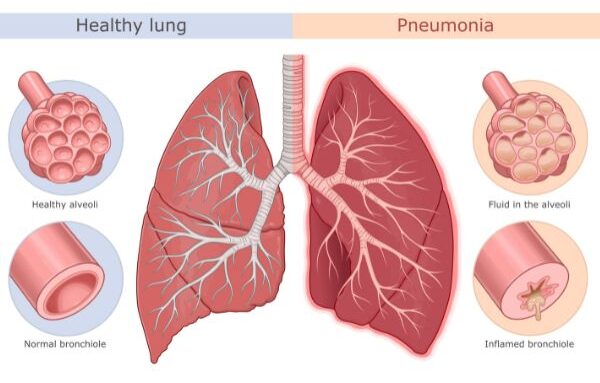
Normal lungs vs pneumonic lungs
How to Prevent Community-Acquired Pneumonia?
Pneumonia can be prevented by adopting the following ways:
Vaccination
Vaccination is our first line of defense against infectious diseases as it prepares the body to fight invading germs. Two notable vaccines employed to prevent pneumonia include the following:
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine or Prenvar
For pneumonia, the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is available which is also known as Prevnar or PCV13. This pneumonia vaccine is particularly suitable for children younger than 2 years of age or those who are above 2 years of age but are more prone to pneumonia due to certain medical conditions.
Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine or Pneumovax
Another pneumococcal pneumonia vaccine known as pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine, Pneumovax, or PPSV23 is suitable for both children above 2 years of age as well as the elderly. It can be administered in the following cases:
| Age Groups | Underlying Medical Conditions | Vaccine Suitability |
| Under 2 years of age | Without any medical condition | Prenvar |
| Above 2 years | With medical conditions | Prenvar |
| 2 to 64 years | Diabetes,
Chronic lung, kidney, or heart disease, Surgical removal of spleen |
Pneumovax |
| 19 to 64 years | Smoking | Pneumovax |
| Above 65 years | With or without any medical condition | Pneumovax |
Apart from vaccination, you can also save yourself from pneumonia by lifestyle changes such as:
- Practice good hygiene
- Wash your hands before a meal
- Cover your mouth and nose while sneezing or coughing
- Having a balanced meal with good-quality ingredients
- Doing regular exercise
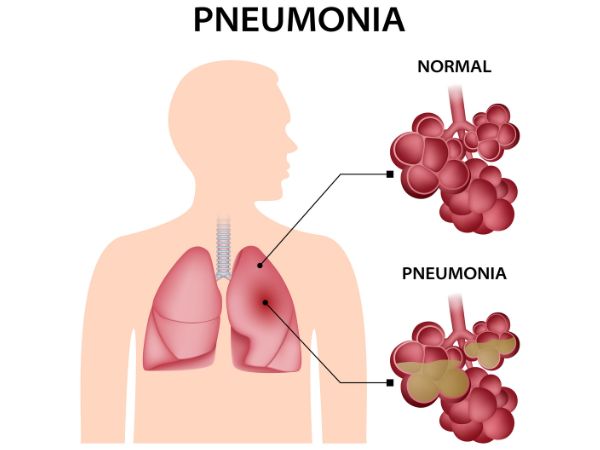
Pus is visible in the alveoli of patients with severe pneumonia
The products mentioned in this article for the management of pneumonia, along with many other medical supplies, can be ordered from Health Supply 770, a reliable name when it comes to medical products. They have a 30-day money-back guarantee and provide your products to you in the shortest possible time. Click the link given in the article to check out the wide range of medical supplies.
Bottom Line
Pneumonia is an infectious respiratory disease that affects the lungs and fills them with liquids or pus. As a result, the fluid-filled alveoli become unable to exchange gases and thus the patient feels troubled breathing during this state of severe illness. The causes of pneumonia can be bacterial, viral, or even fungal. However, the symptoms of the disease are similar in all three cases.
Once properly diagnosed, pneumonia is a treatable condition. The patients are prescribed aspirin, ibuprofen, acetaminophen, oral antibiotics, or antifungal medications depending upon the causative agent as well as the symptoms. In addition, home-based remedies are also advised. However, some patients also require hospitalization. With practicing proper hygiene, pneumonia can also be altogether avoided.
For purchasing top-quality oximeters and other necessary products for respiratory support during pneumonia, reliable vendors like Health Supply 770 should be approached. They ensure the provision of quality products along with satisfactory services.
References
https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/pneumonia.htm
Purchase Pulse Oximeters from Health Supply 770 Shop
 |
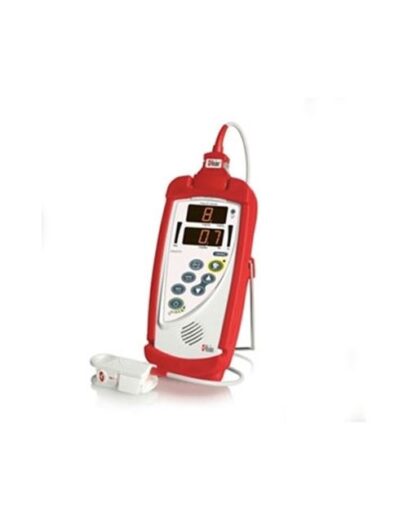
MASIMO CORPORATION 9500 MASIMO RADICAL-7 PULSE OXIMETRY MONITOR EACH |
| Manufacturer: Masimo Corp
Application: Handheld Pulse Co-Oximeter Price: $2,429.99
SHOP NOW https://hs770.com/product/masimo-corporation-9500-masimo-radical-7-pulse-oximetry-monitor-each/ |
 |
Masimo 9216-U – OXIMETER, HANDHELD, RAD57, EACH |
| Manufacturer: Masimo Corp
Application: Handheld Pulse Co-Oximeter Price: $1,438.88
SHOP NOW https://hs770.com/product/masimo-9216-u-oximeter-handheld-rad57-each/ |
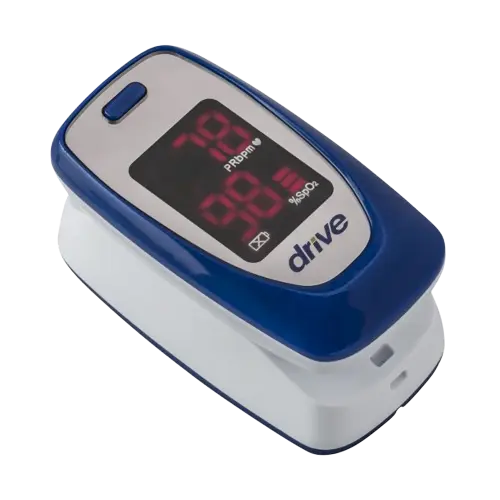 |
Drive Medical Fingertip Pulse Oximeter |
| Manufacturer: Drive Medical
Application: Measurement of oxygen saturation Price: US$46.89
SHOP NOW https://hs770.com/product/drive-medical-mq3000-fingertip-pulse-oximeter/
|