12-Lead ECG Placement Guide by Health Supply 770

ECG is one of the widely run tests for the estimation of cardiac performance in the patient. It is a reliable process that can, at the initial level, can detect a problem in the cardiac rhythm thus manifesting a cardiac issue. While conducting electrocardiography, the placement of the electrodes on different parts of the body is crucial in order to detect and record the signals which further give an indication of the condition of a patient’s heart. Without these electrodes, the test is of no use as there remains no component for the identification as well as quantification of the cardiac signal. To master this essential skill, Health Supply 770 provides a 12-Lead ECG Placement Guide. It will walk you through the precise steps for placing all ten electrodes to ensure you capture clear and dependable cardiac signals every time.
Types of ECGs
ECG, based on the number of electrodes being employed, is of three types which include:
- 12-Lead ECG
- 5-Lead ECG
- 3-Lead ECG
The superiority of 12-Lead ECG over other types
This 12-Lead ECG method is superior to other types of ECGs due to its following properties:
- High sensitivity
- High specificity
- Data reliability
- Accuracy of measurement
Electrodes used in different types of ECG tests
Among these 3 types of ECG, the most important one is the 12-Lead ECG as it gives maximum data about the cardiac condition. Let us take a look at the 12-Lead ECG as well as the method of placing 12-Lead ECG electrodes on the body in detail.
12-Lead ECG
The 12-Lead ECG, named due to the 12 leads obtained as a result of the test, is conducted using 10 electrodes which are set onto several body tissues. 6 of these electrodes are placed on the chest area while the rest of the 4 are fixed on the soft tissue of the limbs.
Positioning of 12-Lead ECG electrodes
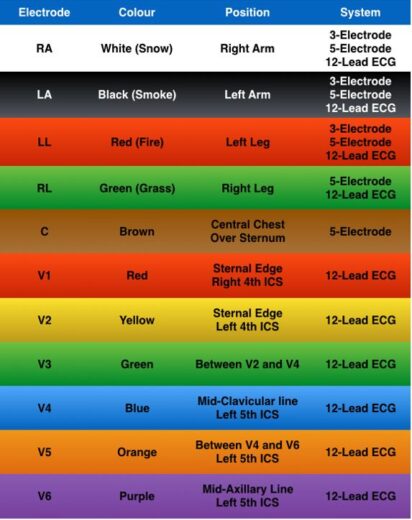
The electrodes used in 12-Lead ECG, along with their placement, are as follows:
| Electrodes to be placed on the chest | Position of their placement |
| V1 | 4th intercostal space to the right of the sternum |
| V2 | 4th intercostal space to the left of the sternum |
| V3 | Directly between the leads V2 and V4 |
| V4 | 5th intercostal space at midclavicular line |
| V5 | Level with V4 at left anterior axillary line |
| V6 | Level with V5 at the midaxillary line |
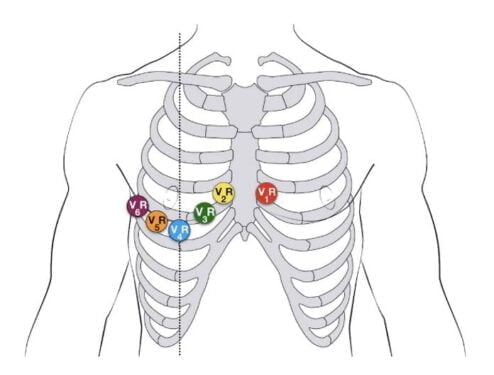
Placement of 6 electrodes of 12-Lead ECG on the chest
| Electrodes to be placed onto the limbs | Position of their placement |
| RA | Upper right arm |
| LA | Upper left arm |
| RL | Lower right leg |
| LL | Lower left leg |
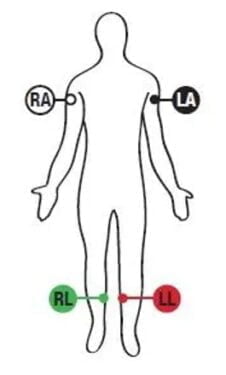
Placement of 4 electrodes of 12-Lead ECG on the soft tissues of the limbs
Placement method of 12-Lead ECG electrodes
In order to place the 12-Lead ECG electrodes properly, the following steps must be kept in mind:
Prepare the patient: Before the start of electrode placement, ask the patient to remove any metallic object such as watch or jewelry. It is also advised to remove the chest hair if necessary. Intake of cold water should be avoided before taking the test. The patient should be asked to relax and remain calm so that the heart rate is not elevated prior to its measurement. Furthermore, the room temperature must not be cold enough to cause shivering the patient.
Preparation of the skin: Sebum or oil is a major component of human skin. This oil, although highly beneficial for the body, can interfere with the electrodes used in an ECG test and generate false results. Therefore, it is necessary to wipe out the maximum oil from the chest area using an alcohol swab prior to placing electrodes.
Mark the spots on the chest and limbs: Once the wiping is done, the points where the 12-Lead ECG electrodes are to be placed must be marked. This pre-marking of the locations helps minimize the time once the electrodes are placed. For the correct placement of the electrodes, the following positioning order must be followed:
- Initially, the placement of V1 and V2 must be done. It is important because all the other electrodes on the chest are placed with reference to these two electrodes. V1 and V2 are placed by locating the patient’s sternum bone. Once it has been found, measure a distance of 4 centimeters below it which will give the location of the 2nd intercostal space.
- Below this point i.e. V2, 3rd as well as 4th intercostal space points can be found and marked. It becomes even easier to locate V4 due to its perfect alignment with the clavicle.
- Once the initial two electrodes are done, the intercostal space between V5 and V6 is located next. For V6, the mid auxiliary point is found and marked. As for V5, it can be marked between V4 and V6.
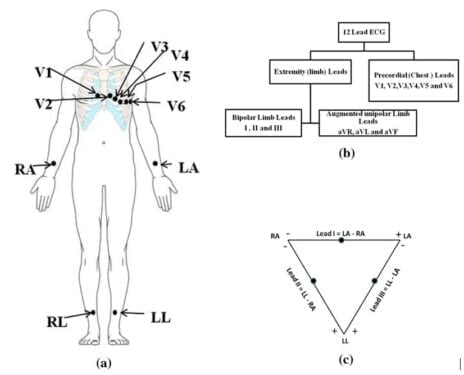
Overall guide for the placement of all the 10 electrodes of 12-Lead ECG electrodes
Place the electrodes: Once all the required points have been marked, the technician can start placing the electrodes one by one at their pre-marked positions.
Run the test: As soon as the placement of all the electrodes is complete, the ECG test can be run and results can be obtained.
Problems associated with 12-Lead ECG machine
While using a 12-Lead ECG, the technician may encounter any of the following problems:
- Battery run-outs
- Detachment of the electrode from the skin
- Disconnection of the leads while the machine is in use
- Hindrance in the wireless data transmission
Conclusion
ECG is one of the most widely used tests which is employed for the estimation as well as quantification of the cardiac anatomical and physiological state. In case of frequently elevated blood pressure, high pulse and heart rate, constant headaches, chest pain, or palpitation, it is recommended to take an ECG test. Among ECG tests, the most reliable and sensitive one is the 12-Lead ECG procedure in which 10 electrodes are utilized to check the condition of the heart. Due to its accuracy of measurement and ease of employment, the 12-Lead ECG is a dominant cardiac test.