OTC Hearing Aids vs. Prescription Hearing Aids: What’s the Difference?
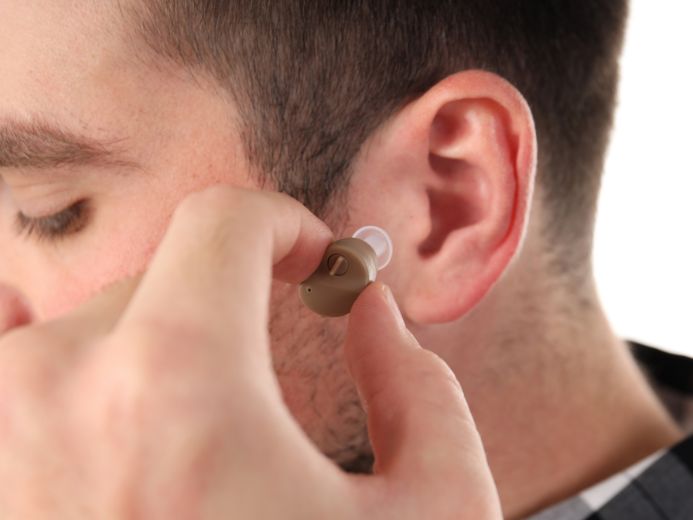
For the first time in the past 50 years, over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids have been allowed to be introduced in the US market after the clearance given by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). These devices can now be purchased without prescription by anyone who feels the need to use them. Moreover, the requirement of mandatory hearing tests which was previously necessary to get a hearing aid prescription has also been eliminated. Despite the increased accessibility to multiple options, one must choose a suitable hearing aid based on age, lifestyle, ear condition, level of hearing impairment, as well as budget. Let us understand the basic difference between the previously existing prescription and OTC hearing aids and find out which one is superior.

Statistics Regarding the Need for Hearing Aid in the US
According to research published by the National Institute for Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, approximately 28.8 million adults in the US need some kind of hearing aid. This number is inclusive to people between the ages of 20 to 69 years.
However, it has been estimated that only 16% of the above-mentioned people actually use a hearing aid. This gap in the need for hearing aids and their employment can be attributed to the high cost of hearing devices as well as the need to see a healthcare provider to get one.
The introduction of OTC hearing aids can bridge the gap and increase accessibility to necessary medical devices.
Prescription Hearing Aid
To get a prescription hearing aid, one has to make an appointment with a hearing healthcare professional or licensed audiologist who, after checking the hearing disability-associated condition, will recommend a hearing test.
Based on the results, a suitable hearing aid is recommended which is then fitted by an expert. Basic types of prescription hearing devices include the following:
● Receiver-in-canal (RIC) hearing aids
● Behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aids
● Invisible-in-canal (IIC) hearing aids
OTC Hearing Aid
Accessing an OTC hearing aid does not require the services of a healthcare provider at any stage. A person can take an online hearing test to find out the level of hearing impairment. These tests are, however, not accurate enough to diagnose a severe medical condition. Although minor issues and ailments can be detected.
For those living in the US who experience mild to moderate hearing loss, over-the-counter or OTC hearing aids can now be purchased from a local retailer or online. These devices can easily be purchased from:
● CVS
● Walmart
● Walgreens
Characteristics Features of OTC Hearing Aid
Over-the-counter hearing aid devices depict the following characteristic features:
● OTC hearing devices are classified in FDA-cleared class II which includes items with self-fitting air conduction.
● With an output nearing 117 decibels (dB), the OTC hearing devices are suitable for use in mild to moderate hearing loss.
● These devices get connected to the user’s smartphone via an app that gives the control directly to the consumers.
● At this time, the designed OTC hearing aids are only for adults. As children need more accurate hearing devices with precise adjustments, it is considered best for them to get one on the recommendation of a licensed audiologist.

Limitations of OTC Hearing Aid
Despite being highly accessible and easy to use, the OTC hearing aid also has certain disadvantages which include the following:
● As there is no need for a prescription or a hearing test before purchasing an OTC hearing aid, one may get a device that, instead of improving, further damages the ear.
● Based on the person-to-person variability, an audiologist fine-tunes the hearing aid a person uses. In the case of OTC aid, these settings are hard to be done accurately by oneself.
● OTC hearing devices are only meant for those who suffer from mild to moderate hearing loss. Therefore, people with severe hearing disabilities do not benefit much from them.
● Due to the one-size-fits-all policy, OTC hearing aids are designed in only one or two sizes. Therefore, one may have fitting issues with their device. On the other hand, prescription devices are particularly designed according to a patient’s individual needs.
● Smart features like programmable amplification as well as Bluetooth connectivity are absent in OTC hearing devices.
Difference between OTC and Prescription Hearing Aids
OTC and prescription hearing devices vary from each other in the following ways:
| Parameters | Prescription Hearing Aid | OTC Hearing Aid |
| Need of prescription | Yes | No |
| Need of hearing test | Yes | No |
| Selection process | Functional communication assessment by an audiologist | Self |
| Professional help while fitting | Necessary | Not needed |
| Design | Customized discreet options | One size fits all |
| Size range | Vast | Narrow |
| Age appropriation | All are groups | 18+ |
| Suitability | Mild to severe hearing loss | Mild to moderate hearing loss |
| Verification of amplification levels | None | Real ear measurements (REMs) |
| Programmable amplification | Present | Absent in most cases |
| Bluetooth connectivity | Present | Absent in most cases |
| Associated risks | Minimum | Significant |
| Price per pair | $1,000 to $7,000 | Less than $1,000 |
| Return policy | Mandatory | Not proposed by the FDA |
All kinds of medical devices and equipment, along with many other medical supplies, can be purchased from Health Supply 770, a reliable name when it comes to medical products. They have a 30-day money-back guarantee and provide your products to you in the shortest possible time.
Conclusion
Hearing is one of the five basic senses which enables us to communicate and socialize. Unfortunately, a large number of Americans are unable to enjoy a normal life owing to some kind of disability which results in mild to severe hearing loss.
Previous methods of accessing a hearing aid have been modernized by the introduction of over-the-counter hearing devices which can be selected based on personal preferences as well as the budget.
Although these OTC hearing aids do not equalize with the prescription ones in terms of efficacy, accessible hearing aid is still a great initiative for many people who cannot afford customized prescription devices.